How is the SDN network different from traditional network architecture? What are Cisco Solutions for SDN networks? What is a Cisco SDN Solution for WAN Networks? and most importantly, How is the Cisco SD-WAN architecture? These are the questions that will be answered in this section.
SDN Network versus Traditional Network Architecture
The first question: how does the SDN network differ from the traditional network architecture? As you know, the operation of traditional network devices consist of three main sections. management-plane that enables us to configure devices via Telnet, SSH, HTTPS or API. Control-plane that enables devices to learn the path to reach to destinations, such as OSPF, BGP and many other protocols. And data-plane that forward incoming traffic with highest possible speed and capacity.
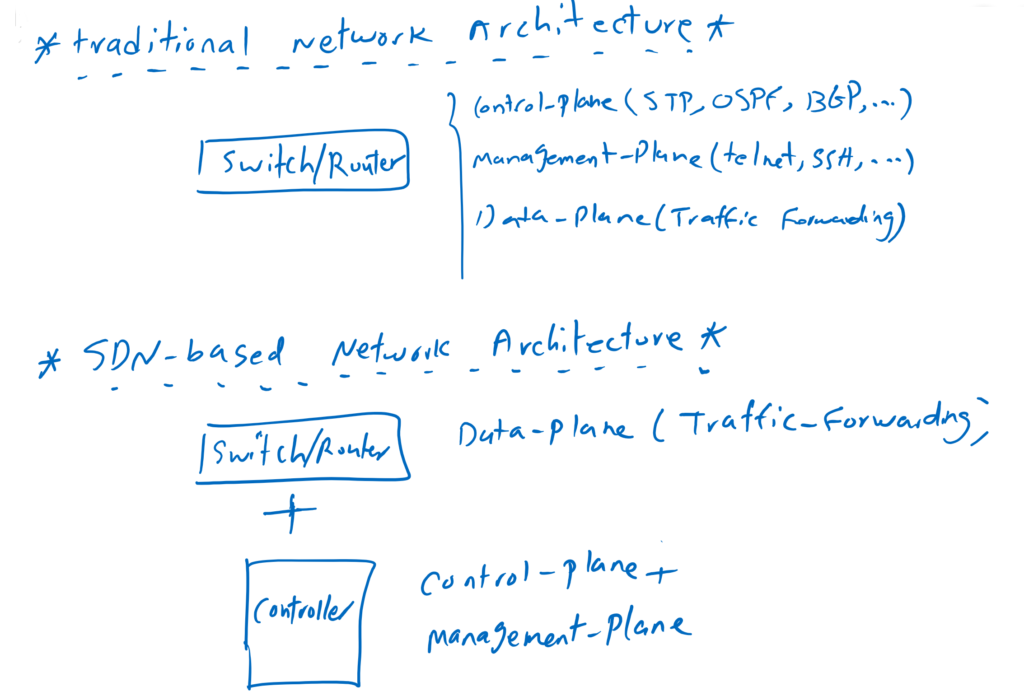
In SDN-based networks, the control plane and management plane parts of network devices are now in a software called SDN controller. And network devices only forward traffic based on the forwarding table and policies pushed by the SDN controller. although that is the ideal definition of an SDN-based network. but in reality, we are going to be as close as possible to this definition.
SDN Controller versus NMS
You may be wondering what is different about SDN controllers with NMS (Network Management System)? I see the differences in two parts. With NMS you manage devices centrally, but the control plane is still located in network devices and NMS only helps us to manage devices centrally and more easily.
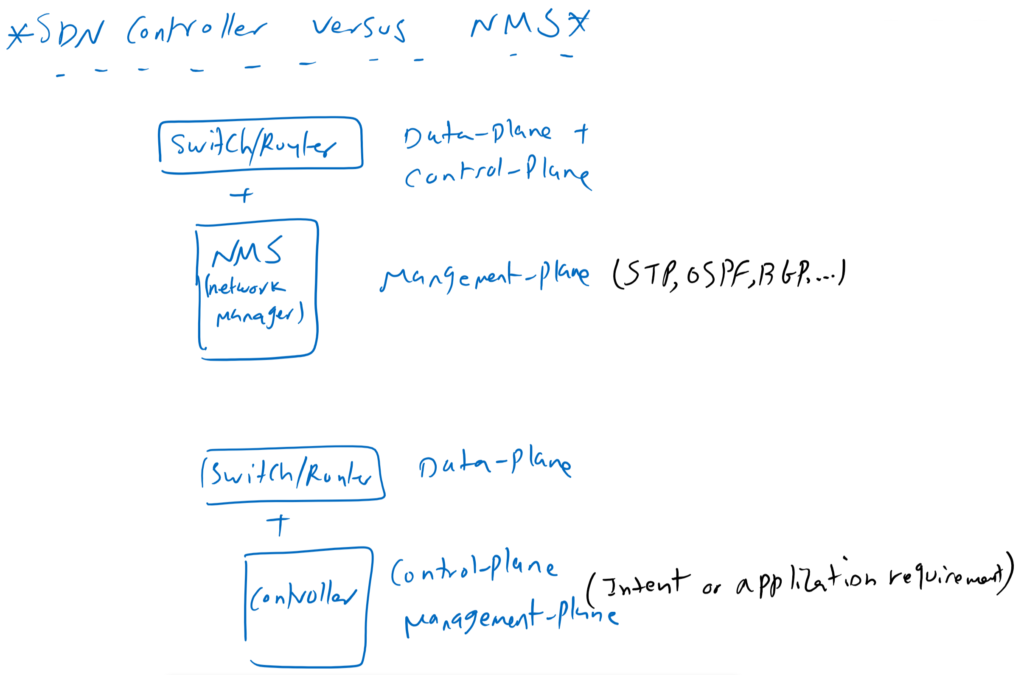
Another difference, however, is that with NMS you still manage and configure, network technologies such as OSPF, BGP and IPSec. In the SDN controller, however, you are less involved in these technologies and mainly configure your intention of network communication and communication requirements of applications. Network technologies are automatically carried out in the background by the SDN controller.
Intent based networking? Application aware Networking?
What do I mean by intent or application requirement? In traditional WAN networks, for example, we configure very complex technologies such as NHRP, mGRE, IPSec, Routing protocols and QoS solutions to enable end-to-end secure and high-quality communication.

But with Cisco SD-WAN we are less involved with background technologies. We only configure the required WAN communication topology, for example if it is hub-and-spoke or full mesh or any other topology. We also configure which of our applications require which quality such as bandwidth or delay.
Therefore, we only configure our intent, and background technologies are automatically carried out by the SDN controller, which largely isolate us from traditional network technologies.
cisco solutions for SDN networks
So what are cisco solutions for SDN networks? Now cisco has three SDN solutions for different part of the network. for LAN & Wireless, cisco has SD-Access solution which is implemented by Cisco DNA Center as SDN Controller. For Data Center, Cisco has cisco ACI Solution (Application Centric Infrastructure) in which APIC plays a role as SDN Controller. And for WAN which is the main discussion of this course, Cisco has Cisco SD-WAN Solution with has bought from Viptela company.

In continue we will discuss more about the Cisco SD-WAN solution and architecture.
Architecture of the Cisco SD-WAN solution
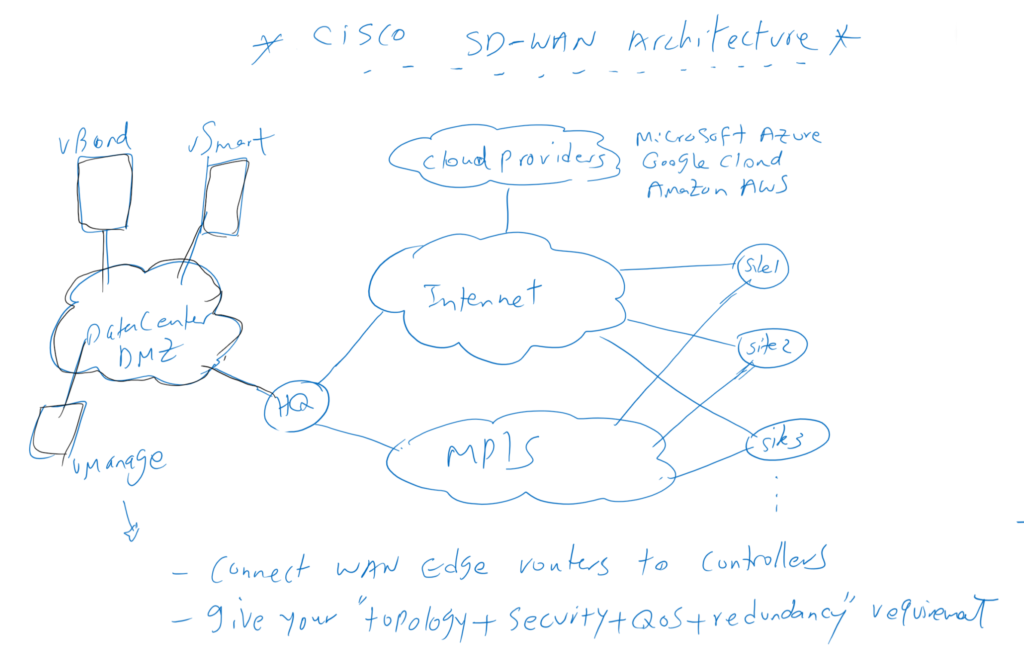
Now let’s discuss the components and architecture of the Cisco SD-WAN solution. Cisco SD-WAN network like any other network consist of data-plane, control-plane and management-plane. data-plane or traffic forwarding is the task of WAN routers which are distributed in main office and branches. But control-plane and management-plane are the task of SD-WAN controllers which is more than one software and We’ll talk about it in continue.
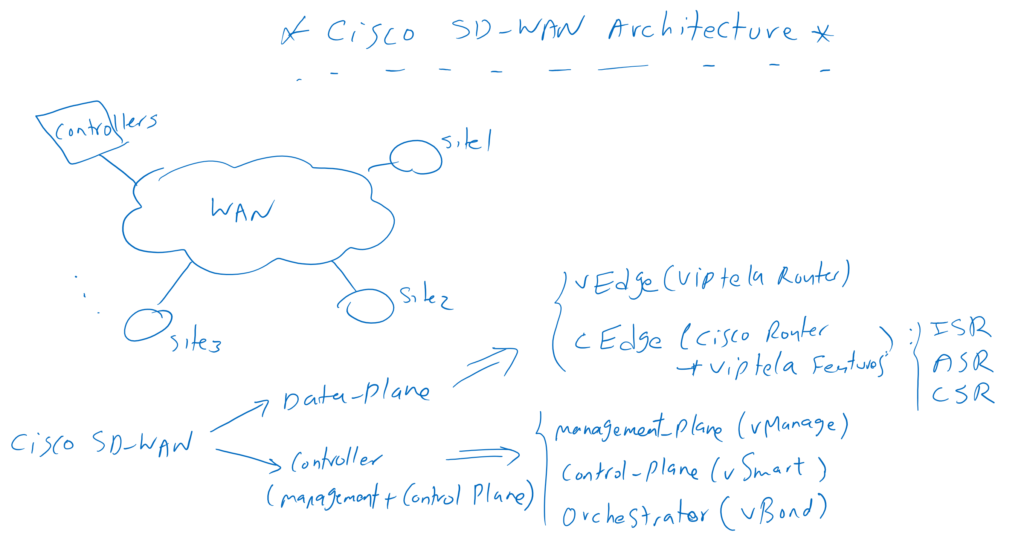
We have two options for the router or data plane part of the SD-WAN network. we can use the native Viptela vEdge WAN router which was purchased from Cisco and it is a virtual router. Or we can use Cisco hardware IOS XE based routers such as ISR, ASR and CSR routers that are extended with the Viptela vEdge software.
The Cisco SD-WAN controller is more than a piece of software.
vManage is a software that we use to configure and manage our SD-WAN network as management-plane pat of the controller. During this course we will work with this software.
vSmart is control plane part of SD-WAN controller. creating IPsec connections between the WAN routers over different underlay transport and handling the routing are the main tasks of the vSmart software. OMP is the name of the routing protocol used by vSmart in the network, which is similar to BGP but developed by the Viptela company.
vBond is another part of the controller software. This is the first point of contact for WAN routers to join the SD-WAN network. vBond must be accessible publicly to all WAN routers and is usually accessible over the Internet. When a new WAN router comes on the network, it first establishes a secure connection with vBond, and then through vBond, WAN routers are trusted with vSmart and vManage to establish a secure connection and be part of SD-WAN network.
as you see, we have more than one controller in the SD-WAN network. vManage, vSmart and vBond are the necessary components of controllers in the SD-WAN architecture.
Traditional WAN Network versus SD-WAN Architecture
To better understand what you achieve by migration to SD-WAN Architecture, suppose we have a company with one main office and many branches which are connected to each other through both MPLS and Internet connectivity.
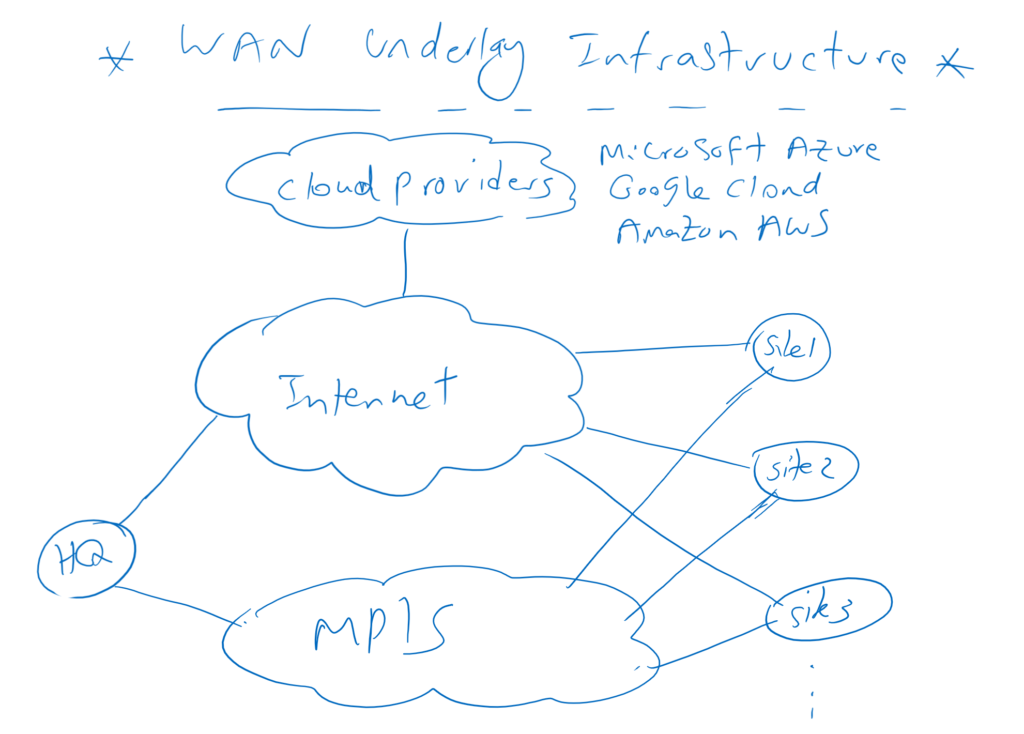
Some of our services are hosted by cloud providers such as Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud or Amazon AWS. Therefore, cloud providers are one of our most important branches that are connected to the Internet and must be accessible to all other branches.
In order to have end-to-end secure and high-quality communication between clients and servers through different WAN connectivity, in traditional WAN architecture, we have to implement a maximum of two DMVPN overlay networks with the help of complex technologies such as NHRP, mGRE, IPSec and routing protocols.
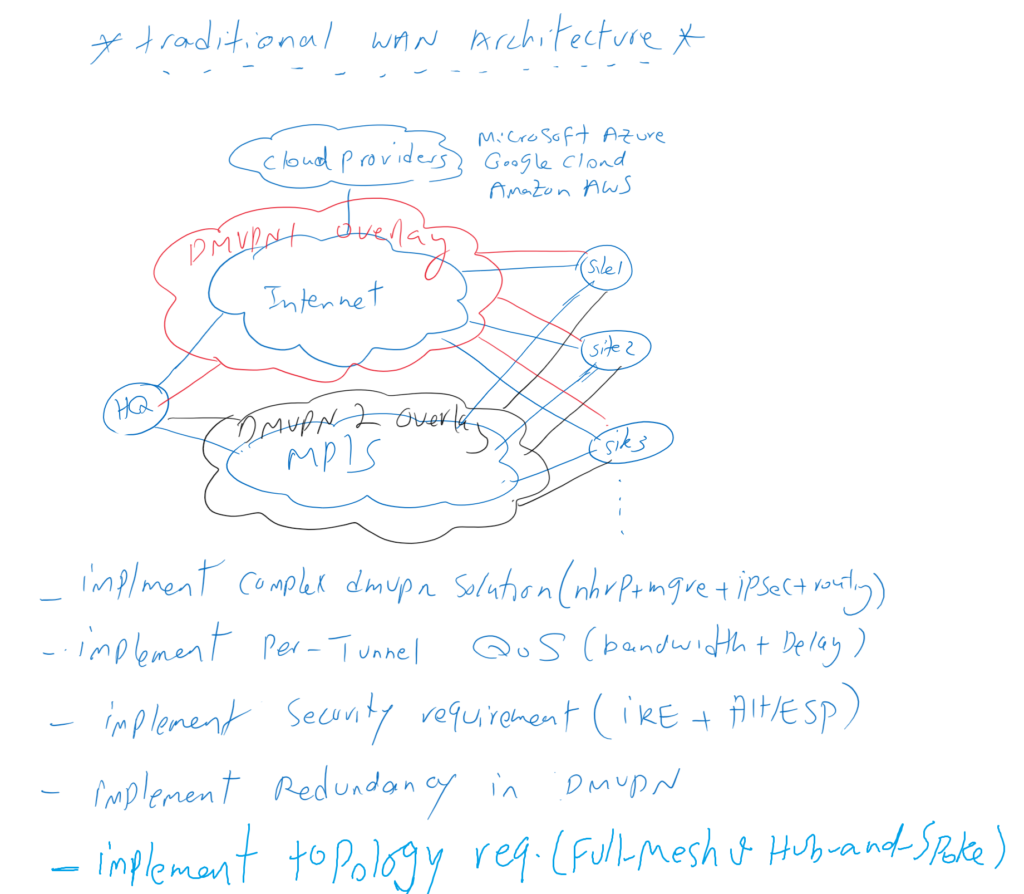
Between every two sites, we have to implement per dynamic Tunnel QoS to guarantee quality of services. Security parameters should be configured based on Application’s security requirement. We are not allowed to forget redundancy. So if one of our transport is disconnected, applications will not be disrupted. Also we have to implement the topology of communication, if it is Hub-and-Spoke, Full-Mesh or any other topology.
As you can see, it is not that easy at all to implement and maintain a WAN network in traditional network architecture.
However, with SD-WAN architecture, you need to install vManage, vBond, and vSmart, and then add and authenticate all WAN routers in those controllers. Then you define your desired intent in terms of topology, security, QoS and redundancy. Configurations are carried out automatically by SD-WAN controllers.
Another Similar Courses: