In the next section we will start to implement SD-WAN infrastructure. therefore in this section we will prepare Cisco SD-WAN implementation guide that shows exactly what we will do in the next steps.
SD-WAN Basic Topology
This is our basic topology, which we will focus on in the next few sections. As you can see we have four sites connected by two different transports, internet and MPLS. Our goal is to prepare end-to-end WAN overlay communication through the SD-WAN solution.
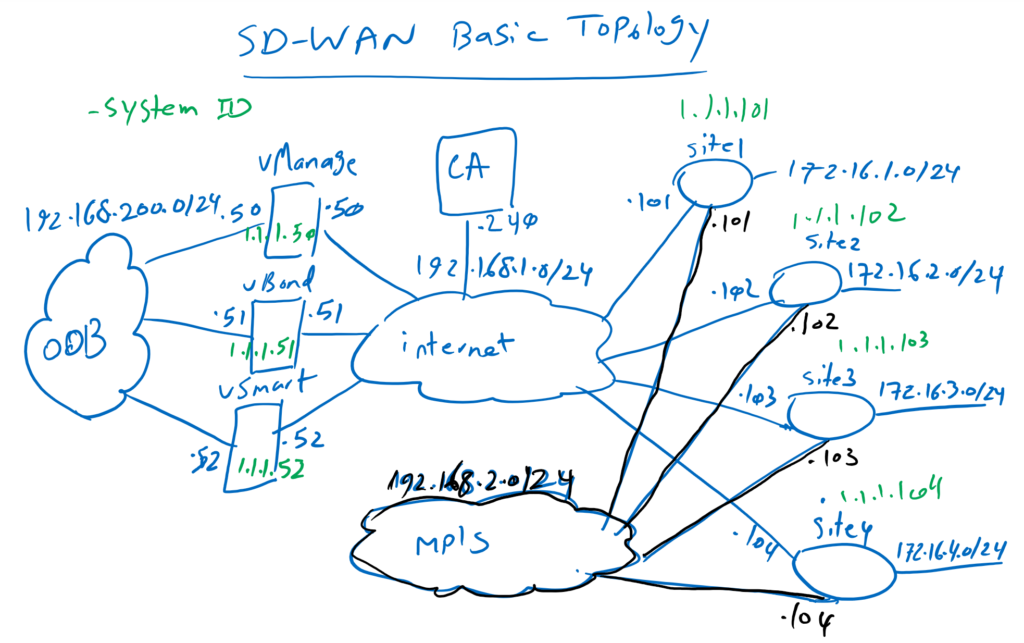
We have three controllers in our topology. In reality, the controllers can be in the DMZ area of our main office and behind NAT since the SD-WAN solution is fully NAT compatible or they can be hosted inside a cloud service provider environment.
In our topology, controllers are for example located in cloud provider environment and they are publicly accessible over internet. 192.168.1.0/24 is IP address range that we have considered for our internet transport. Controllers are also accessible through out of band management (OOB) network. 192.168.200.0/24 is the IP address range that we will configure for out of band management network. .50, .51 and .52 are the last digit of IP addresses of controllers, vManage, vBond and vSmart. both in internet and OOB network.
The IP address range 1.1.1.0/24 is used as the system ID of controllers and WAN routers, which is configured as a loopback address but do not need to be routable.
We have also a CA (Certificate Authority) server to generate certificate for all components of SD-WAN solution including controllers and WAN routers. Certificate is required since it is the main method of authentication between controllers and also WAN routers. 192.168.1.240 is the IP address of our CA server.
We have also a second transport, MPLS, which will be as a redundant transport in our SD-WAN network. 192.168.2.0/24 is the IP address range for our second transport.
Cisco SD-WAN Implementation Guide
What steps will we take in this topology to implement the SD-WAN network?
Step1: Install CA Server for SD-WAN Infrastructure
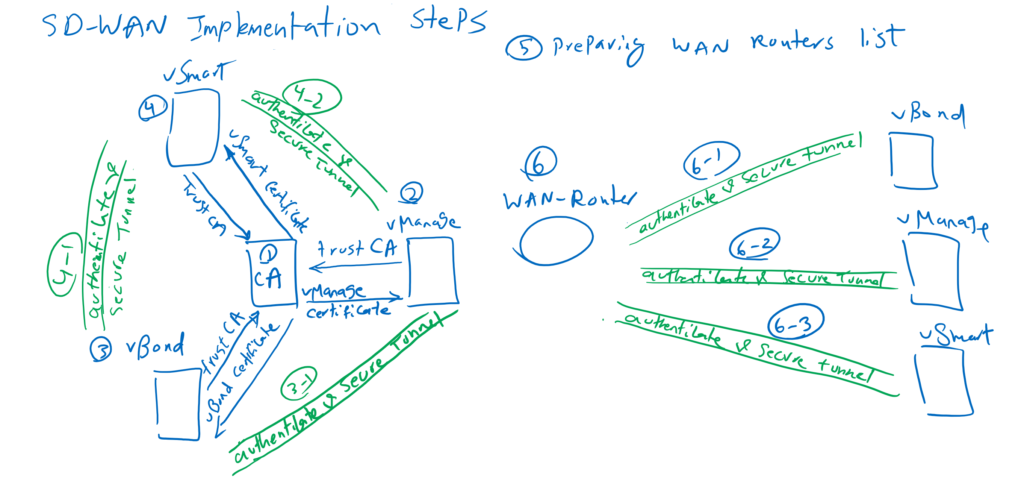
In the first step, we will implement Certificate Authority in windows server 2012 with a specific template for SD-WAN network. So every component in SD-WAN network can trust CA and receive their own certificate. it is required for authentication.
Step2: Install and Configure vManage
In the second step, we will install and configure vManage as management-plane controller in SD-WAN network. through this course, we will configure all our intention through vManage interface. Trusting CA certificate and receiving certificate is the required part of configuration in all controllers and also SD-WAN routers.
Step3: Install and Configure vBond
In the third step , we will configure vBond, which is the initial contact point of WAN routers to join to the SD-WAN network. vBond must be publicly accessible to all other controllers and also SD-WAN routers to orchestrate join process of WAN routers into SD-WAN network.
In vBond, it is also necessary to trust the CA certificate and receive the certificate from the certification authority so that vManage and vBond can authenticate each other and establish a DTLS secure tunnel between each other. All control packets between controllers and also with SD-WAN routers are transmitted through established DTLS secure tunnels.
Step 4: Install and Configure vSmart
In the fourth step, we will configure and install vSmart controller which is responsible for control-plane section of SD-WAN network. IPSec key exchange, creating IPSec tunnel and handling routing are the main tasks of vSmart controller. OMP (overlay management protocol) is the routing protocol used in SD-WAN developed by Viptela company.
Trusting CA and receiving certificate is also necessary in vSmart to authenticate itself to vBond and vManage. vSmart is trusted at first to vBond by authenticating each other and then through vBond, it learns the address of vManage. Then vSmart and vManage authenticate each other and vSmart is added to SD-WAN infrastructure.
By end of this process, we have DTLS secure tunnels between all controllers. All control-plane traffic between controllers will be transmitted through DTLS secure tunnel.
Step 5: Provision WAN Routers
In the next step, we have to install and add WAN Edge routers into SD-WAN infrastructure. but before that, it is necessary to prepare WAN routers list and their licensing in cisco website. Then the list has to be downloaded into SD-WAN infrastructure through vManage, before WAN routers can be trusted in SD-WAN network.
Step 6: Install and Configure WAN Routers
Supposing that we have prepared the list of WAN routers in SD-WAN infrastructure, then we can add WAN routers one by one into SD-WAN network.
SD-WAN routers can be Viptela vEdge or Cisco cEdge routers. Any of Cisco IOS XE devices like ISR, ASR and CSR can be used as cEdge routers in SD-WAN infrastructure, however, extended version of IOS XE must be used to include SD-WAN Viptela features.
In this course because of free licensing limitation, we will use CSR 1000v routers as cEdge routers.
WAN routers connect to vBond as the first point of contact. After they have authenticated each other, the address of vManage and vSmart is transmitted to the WAN router. The WAN router then performs bidirectional authentication with vManage and vSmart controllers. After bi-directional authentication, a DTLS secure tunnel is created between the WAN router and all controllers, which is used for the transmission of configuration updates, key exchanges, OMP routing information updates, and many other management and control packets.
It is worth adding a note here that WAN routers can be automatically added to the SD-WAN infrastructure via the “plug and play” or “zero-touch provisioning” method which will be discussed in this course.
Now SD-WAN network is ready and IPSec secure Tunnel is established automatically between all WAN routers added into infrastructure. But these IPSec Tunnels are only over the first transport. We have to also add our second transport into SD-WAN infrastructure.
Next Steps: Advanced SD-WAN Configurations
then we have to configure our intended Topology, if it is Full-Mesh, Hub-and-Spoke or a custom Topology. Also We have to configure our intended QoS and Security requirements. All these concepts will be discussed and implemented step by step throughout this course.