F5 GSLB (Global Server Load Balancing) is a feature of F5 BIG-IP DNS that allows you to distribute traffic across multiple data centers based on various criteria such as location of the user, server availability and performance, or company policy.
F5 GSLB uses intelligent name resolution to resolve DNS queries and return an IP address to route the user to the data center that is closest to the user or has the best performance or based on company policy.
In this section we will also understand the concept of F5 Wide IP.
F5 GSLB and intelligent name resolution
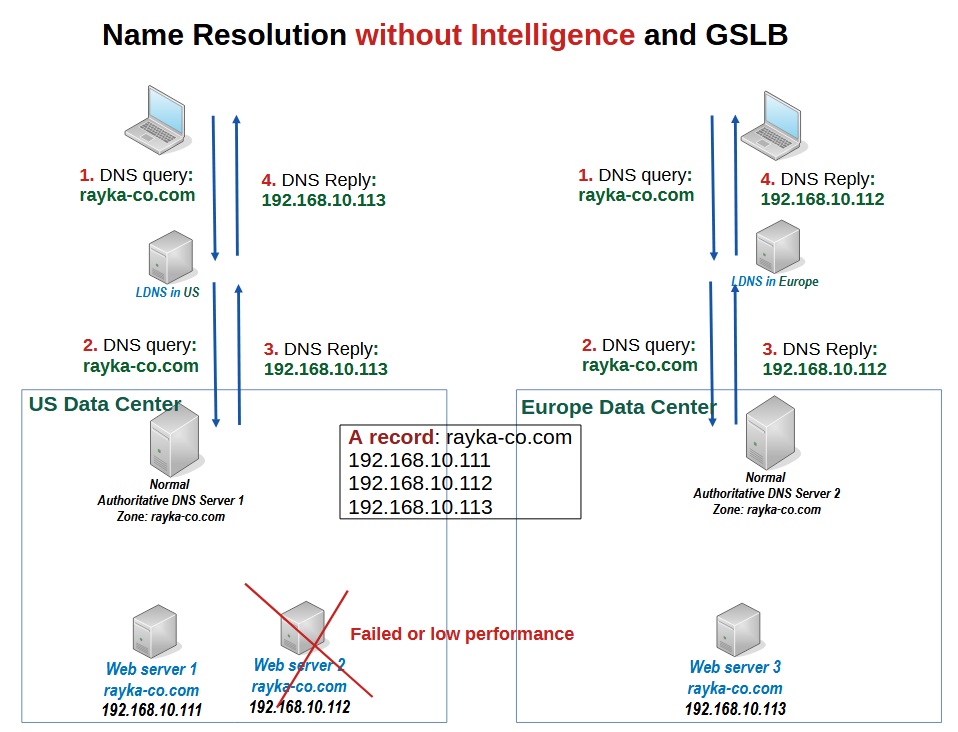
name resolution without intelligence
To better understand how intelligent name resolution works and how it differs from normal name resolution, let’s discuss the following topology.
We have two data centers, one in the US and the other in Europe.
We have three servers, all responsible for the domain “rayka-co,com”. Two of them are in the US data center and one of them is in the European data center with the IP addresses 192.168.10.111, .112 and .113.
We have two DNS servers authoritative for the domain “rayka-co.com”, one in the US data center and the other in the European data center.
These two DNS servers are normal DNS servers like BIND or Microsoft DNS service and have no intelligent functions.
The contents of both DNS servers are the same for the zone “rayka-co.com” and both return three IP addresses for the name “rayka-co.com”, 192.168.10.111, .112 and .113.
DNS servers have no way to check the availability or performance of the servers and data centers, nor do they know where the web servers are located.
So, when a user from the USA wants to access the web service “rayka-co.com”, he sends a DNS query to the local DNS server to find the IP address of the server. The local DNS server sends the query finally to one of the authoritative DNS servers.
Since the DNS server has no idea about the location and performance of the servers, it is possible that it returns the IP address of the web service located in the European data center that is far from the user.
In the same way, a user from Europe wants to access the web server and send a DNS query to a local DNS server in Europe, but he is redirected to a server in the US data center that is down or experiencing low performance due to a hardware problem. This is because authoritative DNS servers have no way to check server availability and performance.
Notice that traffic to the servers are distributed between data centers, called global server load balancing (GSLB), but there is no intelligence in traffic distribution.
GSLB through intelligent name resolution
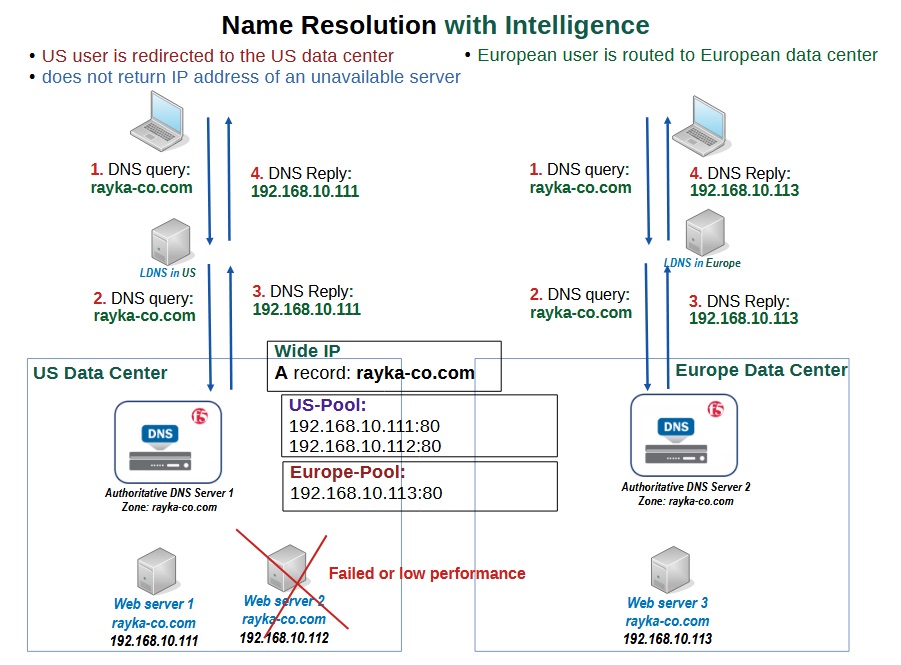
Now that we understand how normal name resolution can be inadequate for GSLB, let’s learn how F5’s intelligent name resolution can enhance GSLB by selecting the best data center for each request.
We have the same topology but we have replaced normal authoritative DNS servers with F5 DNS servers.
In this topology, the US user is redirected to the US data center and the European user is redirected to the European data center, with giving an informed and intelligent response to DNS queries.
Also note that the IP address of the second web server is not returned to the user because F5 DNS always monitors the servers and knows that this server is unavailable or provide a low performance service.
F5 DNS servers need to know the physical and logical topology of the “rayka-co.com” web service in order to direct users intelligently to the nearest or highest performance data center.
In order to make F5 to know the physical topology, we need to configure how many data centers we have and which of the servers are located in which data center.
It is also optional to configure the topology of uplinks and gateways in each data center and how each link connects to the gateway. This is not shown in the topology since it is optional.
In order to also make F5 aware of the logical topology of the servers, we need to create virtual servers, pools and Wide IP.
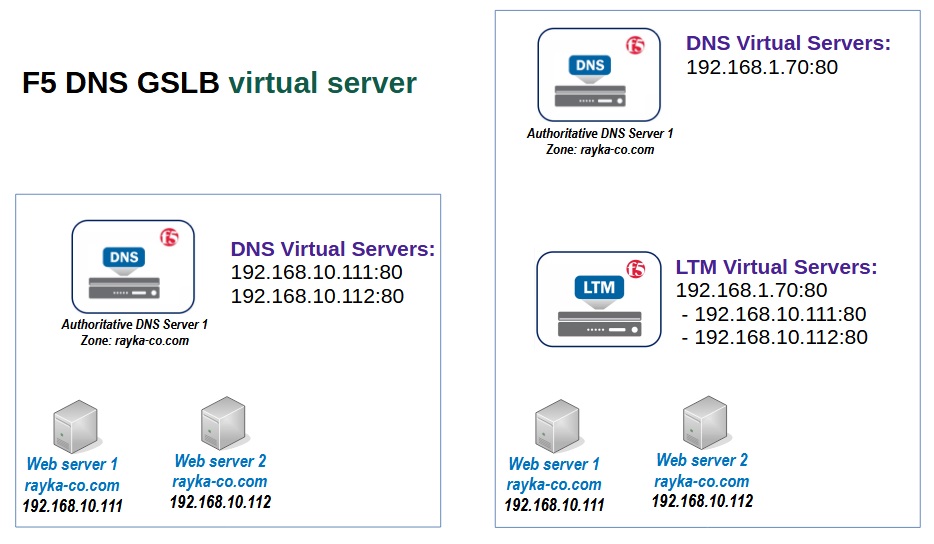
virtual server in F5 GSLB
A virtual server is a logical representation of a physical server that hosts a service of a domain name. A virtual server is identified by an IP address and a port number.
In this topology we have three virtual servers with IP addresses 192.168.10.111, .112 and .113 and port 80 or an HTTP service.
In the next sections we will see that a virtual server can be configured also on F5 BIG-IP LTM in which load balances traffic between servers in the background.
In this case we configure IP address of LTM virtual server as the virtual server in F5 BIG-IP DNS solution.
In this regard, we can say that F5 DNS is used to distribute traffic between data centers and F5 LTM is used to load balance traffic between servers in each data center.
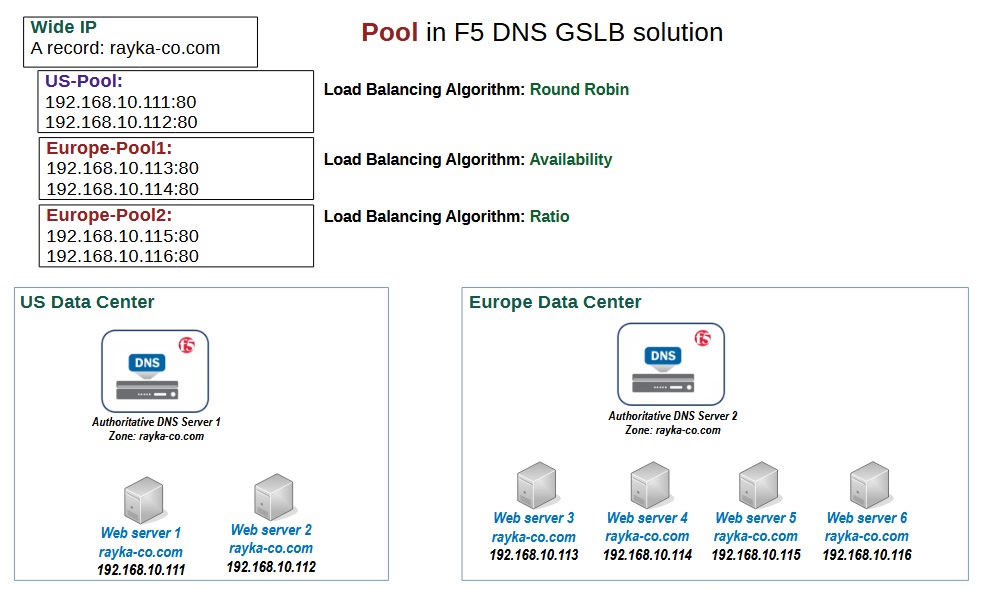
Pool in F5 GSLB
A pool is a group of virtual servers that host the service of a domain name.
F5 DNS uses intelligent name resolution to select the best pool for each request based on various criteria such as availability, performance and location of the servers from the perspective of the user’s local DNS server.
Would you like to know what criteria we use to create a pool? Typically we create a different pool for virtual servers located in different data centers.
In our example, we created two pools, one for a US data center with two virtual servers and one for a European data center with one virtual server.
It’s also possible to create more than one pool for each data center. This is because you can configure a different load balancing algorithm for each pool. Therefore, it is possible to create multiple pools for a data center if you want to use different load balancing algorithms.
For example, you have two virtual servers that you want to act as active standby. This means that traffic will only be forwarded to the second server if the first server is unavailable.
At the same time and in the same data center, there are two other virtual servers on which you want to distribute traffic based on hardware capacity.
Therefore, you create two pools for this data center, with two virtual servers in each pool. The first pool with availability and the second with ratio as a load balancing algorithm.
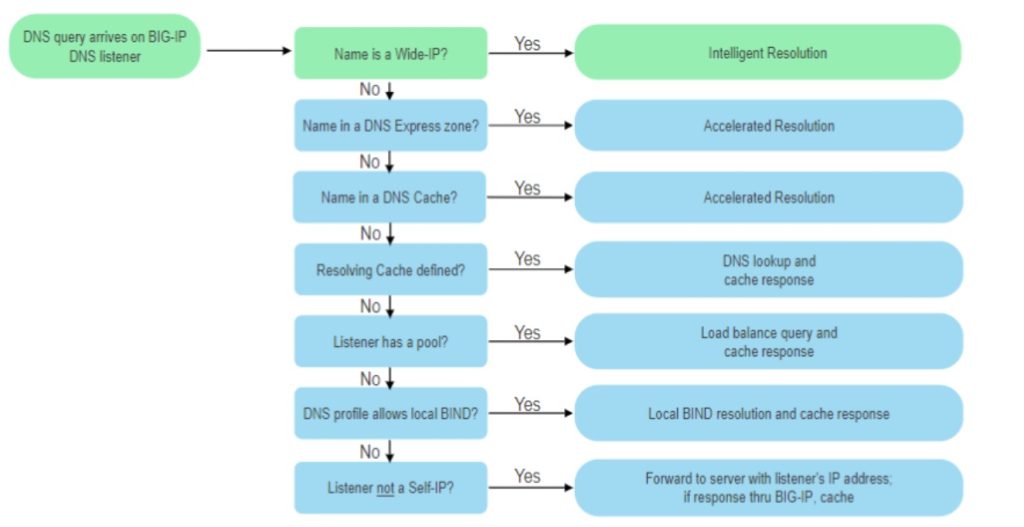
what is F5 Wide IP?
F5 Wide IP is a domain DNS record (not an IP address) that we expect to be resolved using an intelligent name resolution method.
It is assigned to one or more pools of virtual servers that host the content of that domain.
In other words, if we expect a service name to be resolved using an intelligent name resolution method so that traffic is distributed across the data center based on the user’s location, server availability and performance, or traffic policy, we create a DNS record as wide IP.
Wide IP has the highest priority in the F5 DNS resolution process. In other words, if a name exists in the F5 DNS cache or is configured as a DNS Express Zone, is configured as an F5 Local BIND service, and also in Wide IP, F5 DNS uses an intelligent name resolution process to resolve the name.