Juniper SRX security zones provide the ability to assign networks with different security requirements to different security zones, which is a prerequisite for controlling traffic between networks.
It is also possible to control traffic from different security domains to the Juniper device itself and vice versa, from the Juniper device to different security domains, which is a further discussion of this section.
Juniper SRX security zones Fundamental
The first of configuring security policy is to configure security zones and assign interfaces to the zones.
All interfaces with common security requirements are configured in the same security zones. In other words, to control traffic between two security domains, they must be in different security zones.
All traffic between networks in the same security zone are allowed.
In this topology, LAN1 and LAN2 have the same security requirement. therefore they are in the same security zone, Trust.
Interfaces connected to the LAN and WAN have the same security requirements and therefore they are in the same security zone, untrust zone.
Interface connected to the datacenter is located in another security zone, DMZ. zone.
We can control traffic between theses three zones.
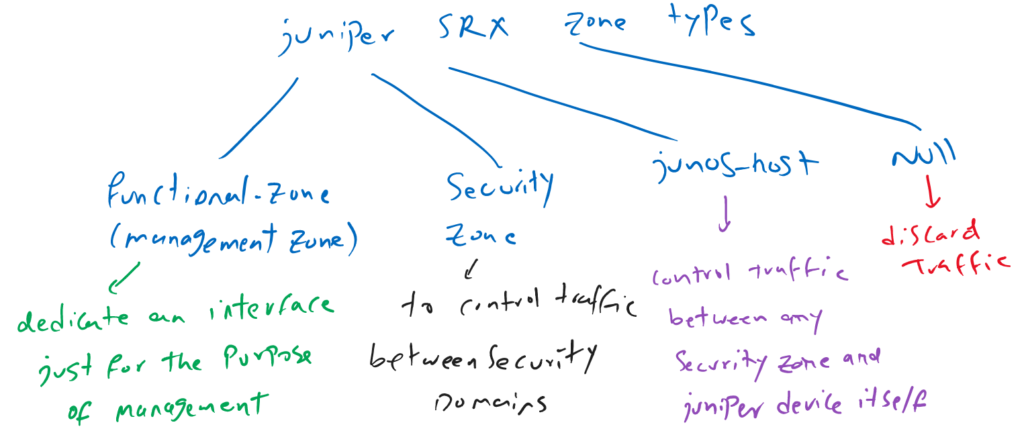
Juniper SRX Zone Types
There are four types of zones in juniper SRX device. “Functional-zone” (management zone), “security zone”, “junos-host” zone and “null” zone.
By default, all interfaces are in the null zone. All traffic received on interfaces in the null zones are discarded. In other words, to start forwarding traffic through an interface, it must be assigned to a security zone.
you can assign an interface to functional management zone. this interface can be used only for the purpose of management like telnet, SSH and web interface.
Traffic cannot be routed and forwarded through the management interface and the destination of management traffic can only be the Juniper device itself.
The use of management zone can be useful in small SRX devices which do not have a dedicated out of band management interface. Therefore you can dedicate an interface just for the purpose of management with assigning it to the management zone.
Junos-host zone is to control traffic between any zone and juniper device itself. By default all traffic from any zone to the juniper device itself are discarded. And all traffic from the juniper device itself to all zones are permitted by default.
Security zone is the main type of zone with security purposes. All interfaces with the same security requirements are assigned to the same security zones. And therefore interfaces with different security requirements are assigned to different security zones.
You are allowed to control traffic only between different security zones.
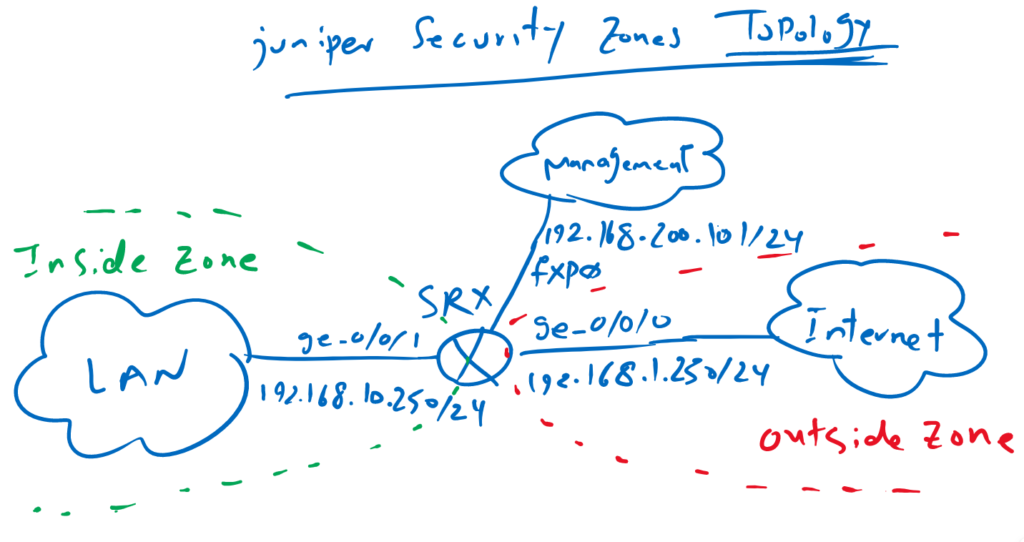
Juniper SRX Zone Topology
This is the topology based on which we will configure security zones.
Juniper SRX is connected to the internet through interface ge-0/0/0 with IP address 192.168.1.250/24. interface ge-0/0/0 will be assigned to security zone “outside”.
Interface ge-0/0/1 is connected to LAN network with IP address 192.168.10.0/24. interface ge-0/0/1 is assigned to security zone “inside”.
Interface fxp0 is management interface in juniper SRX on which we will connect to configure the device. Th IP address of management interface is 192.168.200.101/24.
Preparing juniper SRX device
Before starting the configuration, I have removed all the configuration from juniper SRX device with “request system zeroize” command.
Then I have added these configuration just to initiate the device for remote connection and prepare it for security zone configuration.
> request system zeroize
set system root-authentication plain-text-password
set system login user rayka class super-user
set system login user rayka authentication plain-text-password
set system services ssh root-login allow
set system services telnet
set system services web-management https interface fxp0.0
set system services web-management https system-generated-certificate
set interfaces fxp0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.200.101/24A password is configured for root user.
A new username with root privilege is created.
SSH, telnet and web remote access is activated.
Finally the IP address of management interface is configured to 192.168.200.101/24 as we have displayed in the topology.
Juniper SRX security zones configuration
With command “set security zones ?” in configuration mode, you can see that there two types of zones that can be configured. “functional-zone” and “security-zone”.
rayka# set security zones ?
Possible completions:
+ apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data
+ apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups
> functional-zone Functional zone
> security-zone Security zones
[edit]functional-zone management in juniper SRX
There is only one option with functional-zone and that is management, it means you can assign and dedicated an interface to management interface.
Management interface is just to connect to the device for management purposes.
Management-zone is useful mostly for small SRX devices that do not have dedicated out of band management interface.
Here in vSRX, fxp0 interface is dedicated to management-only purposes.
But just to show how one interface is added to management interface, I add interface ge-0/0/2 to functional-zone management.
rayka# set security zones functional-zone management interfaces ge-0/0/2
rayka# rollback 0 With command “rollback 0”, I will delete management interface configuration, since we do not need it in our topology.
configure security zones and assign interfaces to security zones
With command “set security zones security-zone ?”, you can see that by default there are two security zones “untrust” and “trust” but I will nit use them here and I will create my own security zones, “outside” and “inside” as in the topology.
rayka# set security zones security-zone ?
Possible completions:
<name> Name of the zone
trust Name of the zone
untrust Name of the zone
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone inside
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside After creating security zones, I have to assign interfaces to security zones.
First I, will configure the IP address of ge-0/0/0 and ge-0/0/1 as in the topology. then I will add the interface ge-0/0/0 in outside security zone and interface ge-0/0/1 in inside security zone.
rayka# set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.250/24
[edit]
rayka# set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.10.250/24
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside interfaces ge-0/0/0
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone inside interfaces ge-0/0/1To check the status of security zones, with command “show security zones terse” in operational mode, you can list all configured security zones.
[edit]
rayka# run show security zones terse
Zone Type
inside Security
outside Security
trust Security
untrust Security
junos-host SecurityWith command “show security zones”, you can also check which interfaces are assigned to each security zone.
[edit]
rayka# run show security zones
Security zone: inside
Zone ID: 11
Send reset for non-SYN session TCP packets: Off
Policy configurable: Yes
Interfaces bound: 1
Interfaces:
ge-0/0/1.0
Advanced-connection-tracking timeout: 1800
Unidirectional-session-refreshing: No
Security zone: outside
Zone ID: 10
Send reset for non-SYN session TCP packets: Off
Policy configurable: Yes
Interfaces bound: 1
Interfaces:
ge-0/0/0.0
Advanced-connection-tracking timeout: 1800
Unidirectional-session-refreshing: No
Security zone: trust
Zone ID: 7
Send reset for non-SYN session TCP packets: On
Policy configurable: Yes
Interfaces bound: 0
Interfaces:
Advanced-connection-tracking timeout: 1800
Unidirectional-session-refreshing: No
Security zone: untrust
Zone ID: 8
Send reset for non-SYN session TCP packets: Off
Policy configurable: Yes
Screen: untrust-screen
Interfaces bound: 0
Interfaces:
Advanced-connection-tracking timeout: 1800
Unidirectional-session-refreshing: No
Security zone: junos-host
Zone ID: 2
Send reset for non-SYN session TCP packets: Off
Policy configurable: Yes
Interfaces bound: 0
Interfaces:
Advanced-connection-tracking timeout: 1800
Unidirectional-session-refreshing: No
[edit]
rayka# configure juniper security zone host-inbound-traffic
As I have explained previously, by default, all traffic from any security zone to the juniper itself are discarded but all traffic from juniper device itself to any security zone are permitted by default.
The parameter “host-inbound-traffic” is to configure which traffic are permitted to the juniper device itself.
This parameter can be configured in security zone level or a specific interface in security zone.
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside host-inbound-traffic ...
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside interfaces ge-0/0/0 host-inbound-traffic ...
As we can guess, what is configured in security zone interface level is preferred to what is configured in the security zone level.
There are two parameters in “host-inbound-traffic” section, “protocols” and “system-services”.
With protocols option, you can permit protocol traffics like “OSPF”, “IGMP” and “PIM” to the juniper device itself.
With system-services option, you can allow services like ping, SSH, Telnet and SNMP to the juniper device.
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside host-inbound-traffic ?
Possible completions:
+ apply-groups Groups from which to inherit configuration data
+ apply-groups-except Don't inherit configuration data from these groups
> protocols Protocol type of incoming traffic to accept
> system-services Type of incoming system-service traffic to accept
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside host-inbound-traffic protocols ?
Possible completions:
all All protocols
bfd Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
bgp Border Gateway Protocol
dvmrp Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
igmp Internet Group Management Protocol
ldp Label Distribution Protocol
msdp Multicast Source Discovery Protocol
nhrp Next Hop Resolution Protocol
ospf Open Shortest Path First
ospf3 Open Shortest Path First version 3
pgm Pragmatic General Multicast
pim Protocol Independent Multicast
rip Routing Information Protocol
ripng Routing Information Protocol next generation
router-discovery Router Discovery
rsvp Resource Reservation Protocol
sap Session Announcement Protocol
vrrp Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside host-inbound-traffic system-services ?
Possible completions:
all All system services
any-service Enable services on entire port range
appqoe APPQOE active probe service
bootp Bootp and dhcp relay-agent service
dhcp Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
dhcpv6 Enable Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6
dns DNS service
finger Finger service
ftp FTP
high-availability High Availability service
http Web management service using HTTP
https Web management service using HTTP secured by SSL
ident-reset Send back TCP RST to IDENT request for port 113
ike Internet Key Exchange
lsping Label Switched Path ping service
lsselfping Label Switched Path self ping service
netconf NETCONF service
ntp Network Time Protocol service
ping Internet Control Message Protocol echo requests
r2cp Enable Radio-Router Control Protocol service
reverse-ssh Reverse SSH service
reverse-telnet Reverse telnet service
rlogin Rlogin service
rpm Real-time performance monitoring
rsh Rsh service
snmp Simple Network Management Protocol service
snmp-trap Simple Network Management Protocol traps
ssh SSH service
tcp-encap Tcp encapsulation service
telnet Telnet service
tftp TFTP
traceroute Traceroute service
webapi-clear-text Webapi service using http
webapi-ssl Webapi service using HTTP secured by SSL
xnm-clear-text JUNOScript API for unencrypted traffic over TCP
xnm-ssl JUNOScript API service over SSLAs an example , I will add all protocols and all system services in security zone level to be allowed. But in security zone interface level, I will add only OSPF protocol and I will exempt telnet service from all system-services with “except” parameter.
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone inside host-inbound-traffic system-services all
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone inside host-inbound-traffic protocols all
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside interfaces ge-0/0/0 host-inbound-traffic protocols ospf
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside interfaces ge-0/0/0 host-inbound-traffic system-services all
[edit]
rayka# set security zones security-zone outside interfaces ge-0/0/0 host-inbound-traffic system-services telnet except
[edit]
rayka# show | compare
[edit security zones security-zone outside]
+ host-inbound-traffic {
+ system-services {
+ all;
+ }
+ protocols {
+ all;
+ }
+ }
[edit security zones security-zone outside interfaces ge-0/0/0.0]
+ host-inbound-traffic {
+ system-services {
+ telnet {
+ except;
+ }
+ all;
+ }
+ protocols {
+ ospf;
+ }
+ }
[edit security zones security-zone inside]
+ host-inbound-traffic {
+ system-services {
+ all;
+ }
+ protocols {
+ all;
+ }
+ }
[edit]
rayka# Now we expect that we can ping the juniper device.
C:\Users\raykaremote>ping 192.168.1.250
Pinging 192.168.1.250 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.250: bytes=32 time=3ms TTL=65
Reply from 192.168.1.250: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.1.250: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.1.250: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.250:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 3ms, Average = 0ms
C:\Users\raykaremote>However it not the discussion of this section but just to show you the application of “junos-host” zone, I want to reject “ICMP” traffic to the juniper device but not with “host- host-inbound-traffic”.
I will configure it with writing a security policy from zone “outside” to the “junos-host” zone which is juniper device itself.
set security policies from-zone outside to-zone junos-host policy deny-icmp match source-address any
set security policies from-zone outside to-zone junos-host policy deny-icmp match destination-address any
set security policies from-zone outside to-zone junos-host policy deny-icmp match application junos-icmp-ping
set security policies from-zone outside to-zone junos-host policy deny-icmp then reject
[edit]
rayka# show | compare
[edit security policies]
from-zone trust to-zone untrust { ... }
+ from-zone outside to-zone junos-host {
+ policy deny-icmp {
+ match {
+ source-address any;
+ destination-address any;
+ application junos-icmp-ping;
+ }
+ then {
+ reject;
+ }
+ }
+ }
[edit]Now we expect that we can not ping the juniper device from outside anymore.
C:\Users\raykaremote>ping 192.168.1.250
Pinging 192.168.1.250 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.1.250: Destination port unreachable.
Reply from 192.168.1.250: Destination port unreachable.
Reply from 192.168.1.250: Destination port unreachable.
Reply from 192.168.1.250: Destination port unreachable.
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.250:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),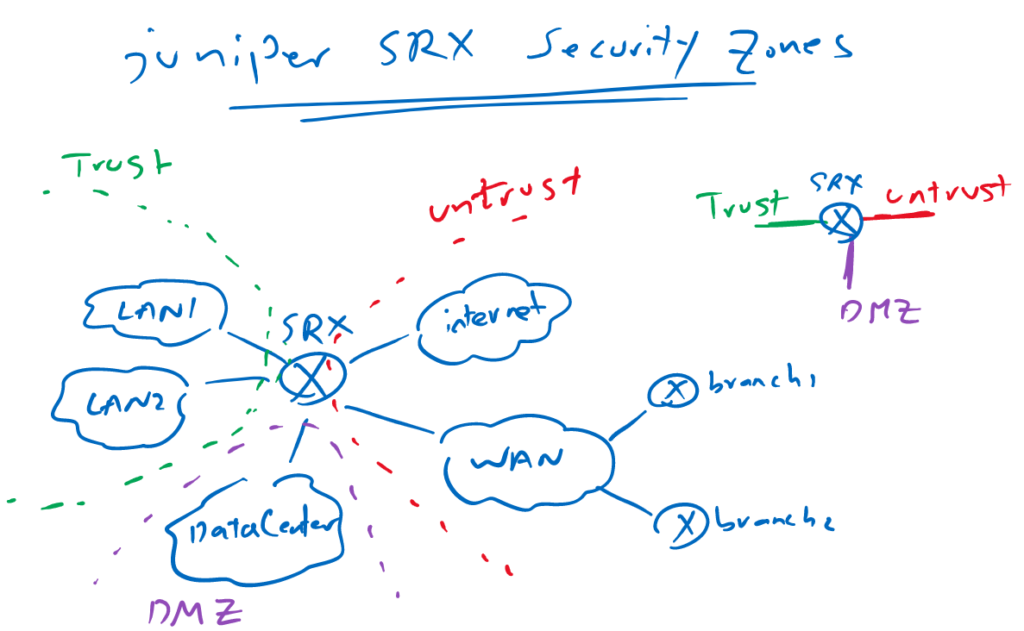
I purchased 3 of your training, the two Juniper JNCIA and JNCIA-SEC and ISIS training. Thank you for the good work you do. I plan to buy the IPV6 Training as well.
Thank you so much for your support and kind words!