Cisco FTD SSL Decryption Policy gives the capability to inspect SSL encrypted contents over the network, otherwise encrypted traffic, such as HTTPS connections, which make up most of the Internet content, cannot be inspected.
what is Cisco FTD Decryption Policy?
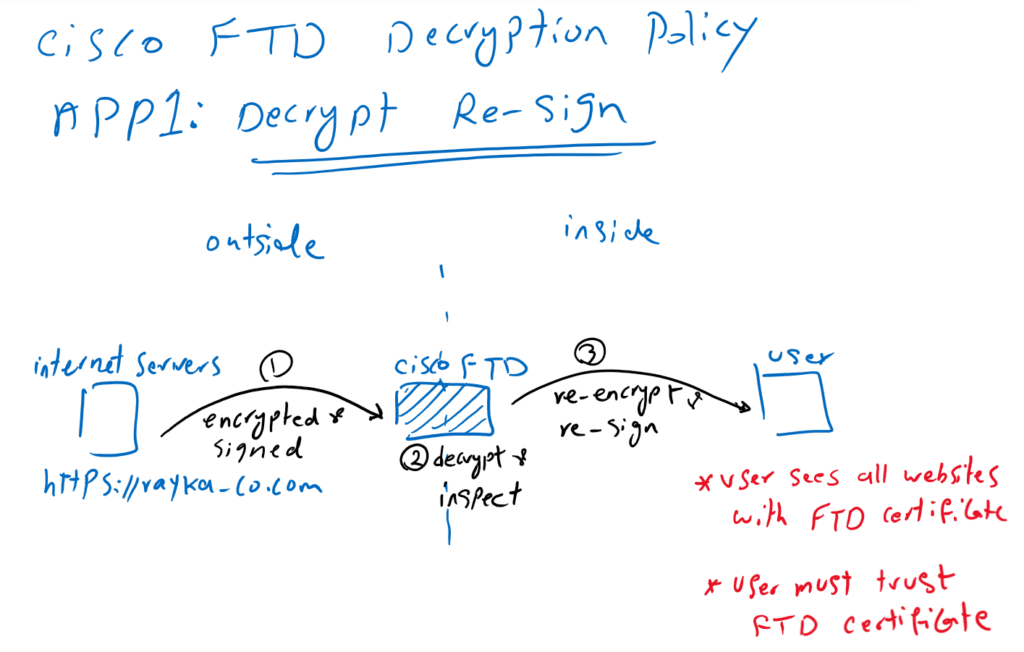
Application1: Decrypt Re-Sign
There are two main application of SSL Decryption policy.
In the first application, when a user inside the network browses an HTTPS website such as https://rayka-co.com, outside the network, the content of the website is decrypted by Cisco FTD so it can be inspected. After inspection, the content is re-encrypted and signed before being forwarded to the user. this method is also called “Decrypt Re-Sign“.
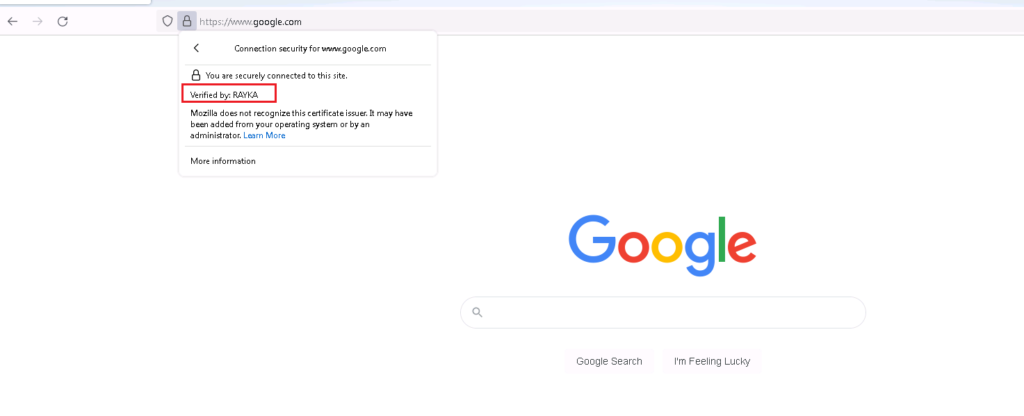
With this method, Cisco FTD gives its own certificate to internal users instead of real server certificates. From the user’s perspective, all websites are trusted by the Cisco FTD certificate. This method requires that users inside the network to trust the Cisco FTD certificate.
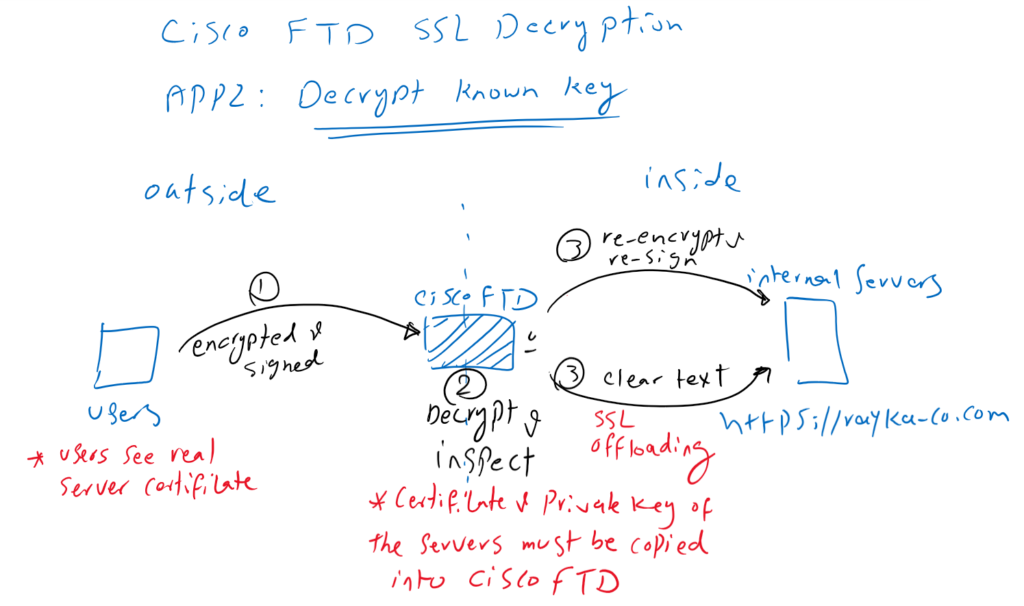
Application2: Decrypt Known Key
In the second application, we are the owner of servers or websites within the network. Users from outside the network get the services from our servers with servers real certificate. In this method, we decrypt the content in Cisco FTD so it can be inspected to prevent any outside malicious content from reaching the servers inside the network. After inspection, the content is forwarded to the servers within the network.
There are two points that we must note.
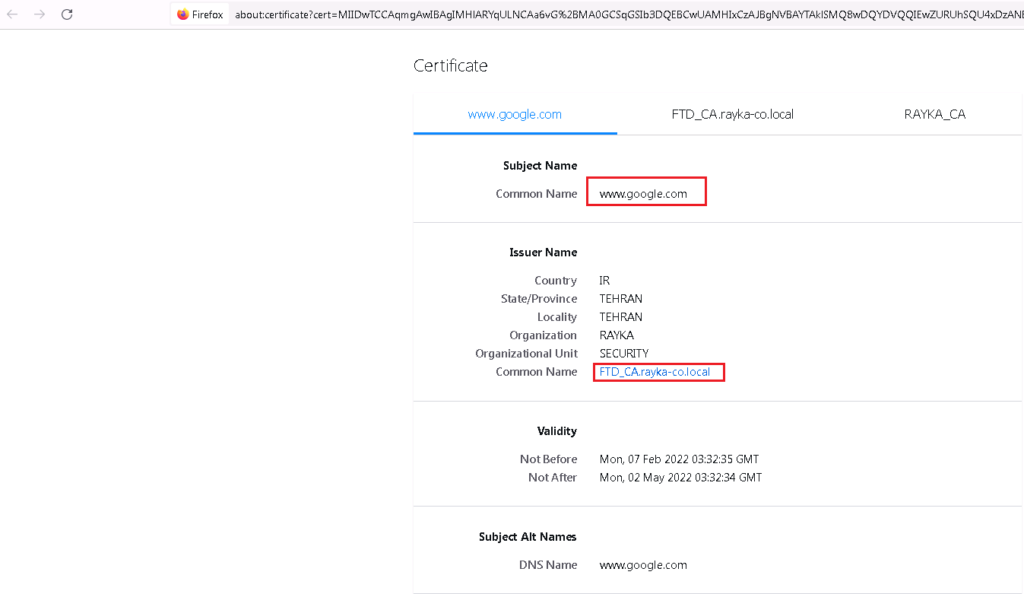
First, Cisco FTD must have server certificate and its private key so that it can decrypt all content from users outside the network to the servers’ destination. for this reason the method is called “Decrypt Known Key”.
The second point is that content from Cisco FTD to the servers can be transmitted in encrypted or clear text. When Cisco FTD forwards the contents to the servers in clear text, it aims to reduce the SSL decryption overhead from the servers. When this is the reason for implementing the SSL decryption policy, it is known as “SSL offloading“.
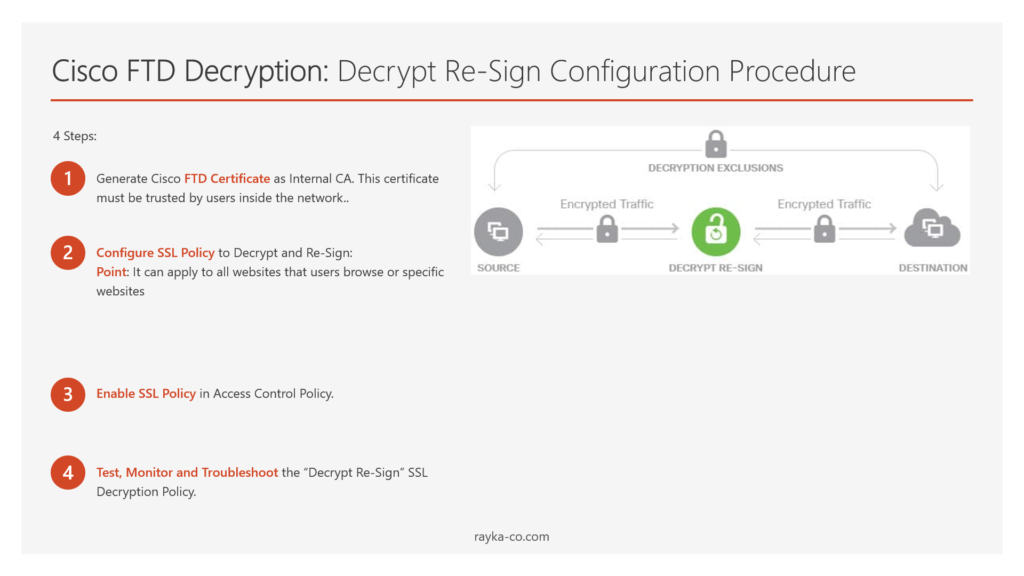
Cisco FTD Decryption: Decrypt Re-Sign Configuration Procedure
There are four steps to implement first type of Cisco FTD Decryption Policy.
- Generate Cisco FTD Certificate as Internal CA
In the first step we generate a certificate for FTD. This certificate is distributed to users within the network instead of real servers certificate. This certificate must be trusted by all users inside the network.
- Configure SSL Policy to Decrypt and Re-Sign
It can apply to all websites that users browse or specific websites
- Enable SSL Policy in Access Control Policy
The SSL decryption policy will not decrypt or inspect any SSL websites until it is activated in access control policy.
- Test, Monitor and Troubleshoot the “Decrypt Re-Sign” SSL Decryption Policy
Then we will browse some HTTPS websites to check the certificate and also monitor the logs and connection events generated by cisco FTD.
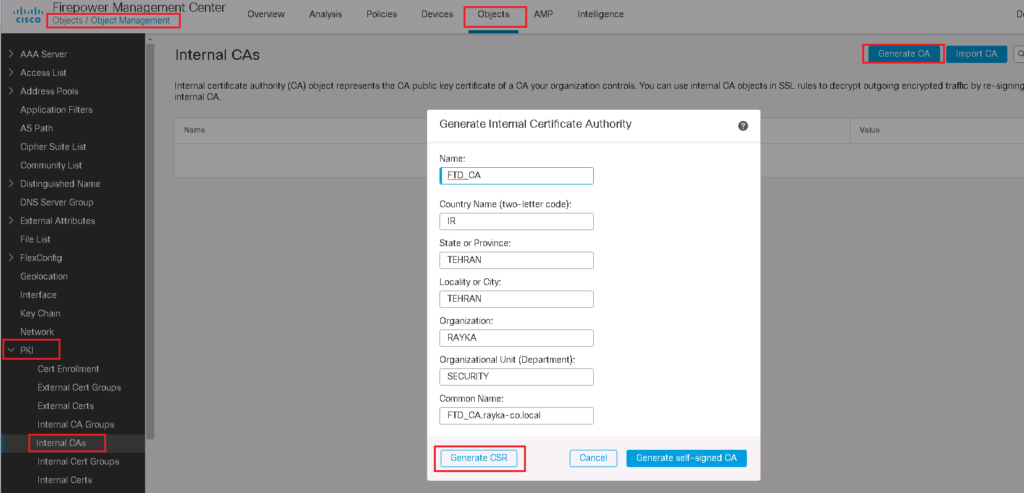
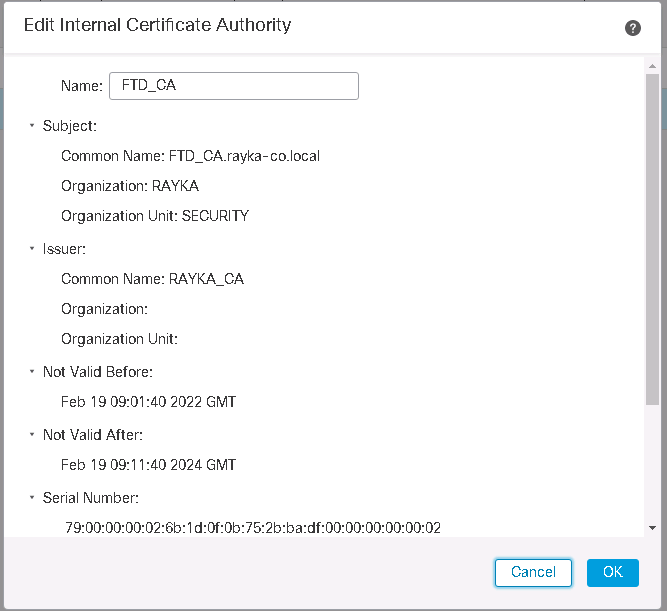
Generate Cisco FTD Certificate as Internal CA
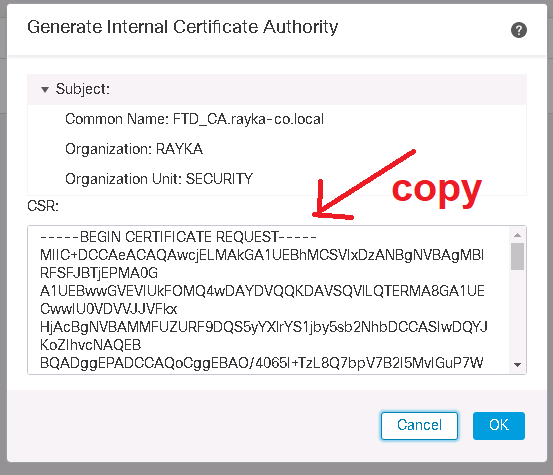
We start by generating a certificate request for Cisco FTD.
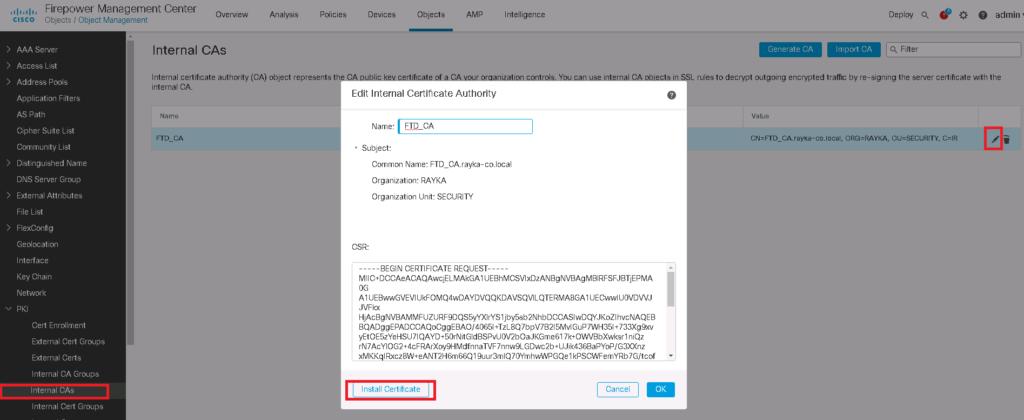
Objects -> Object Management -> PKI -> internal CAs -> Generate CA
This can be generated as a self-signed certificate, which is generally not recommended, but can be used in small and lab environments. If we have an enterprise CA, then FTD generate a certificate request (CSR) which will be forwarded to the enterprise CA to obtain a certificate.
We complete CSR and then request the certificate.
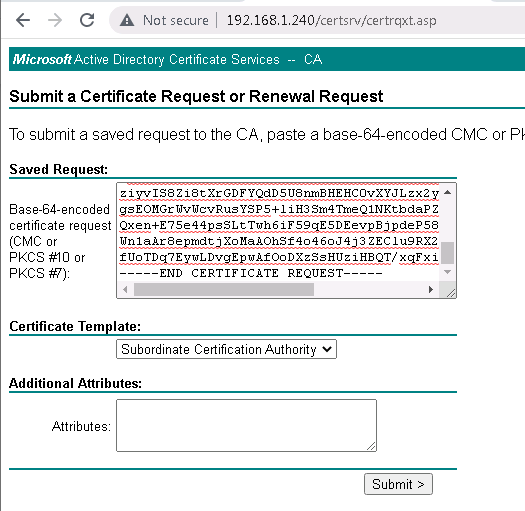
Then the Certificate Request (CSR) must be sent to the CA in order to receive a certificate.
If you do not know how to install CA in Microsoft Server, I have already explained in a video named “3. SD-WAN Certificate Authority Configuration” in SD-WAN course.
CSR should be requested as a “Subordinate Certificate Authority” since Cisco FTD itself acts as a subordinate CA.
http://192.168.1.240/certsrv/ -> Request a Certificate -> advanced certificate request ->
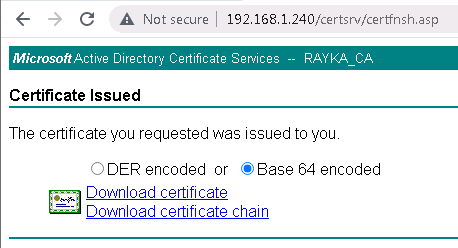
The downloaded certificate must be installed in Cisco FTD.
Notice that enterprise certificate CA must be trusted by FTD since it has signed already FTD certificate.
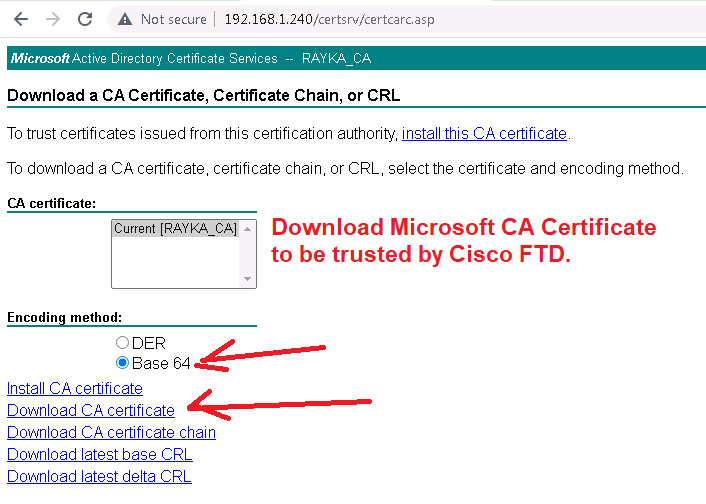
To do this, we download the CA certificate from Microsoft CA and add it to the “Trusted Certificate Authority” in Cisco FTD.
http://192.168.1.240/certsrv/ -> Download a CA certificate, certificate chain, or CRL -> Download CA certificate
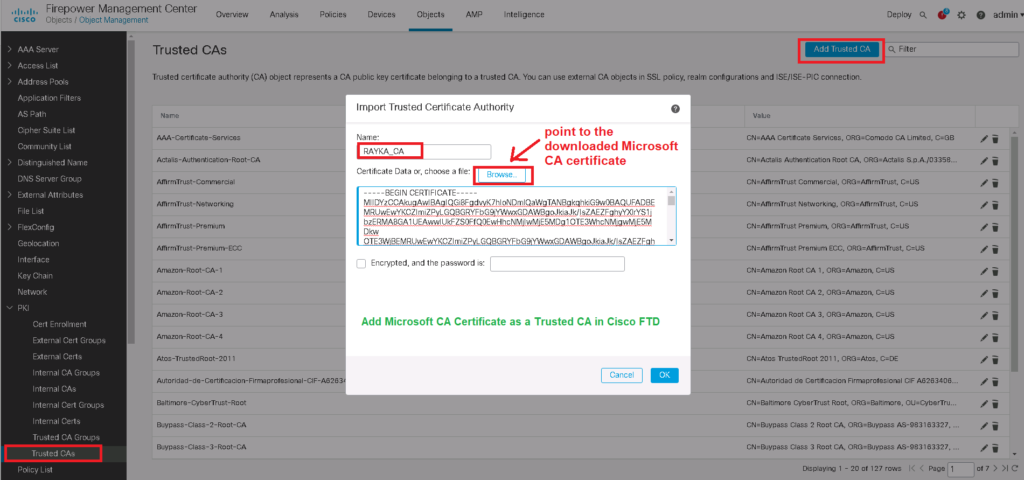
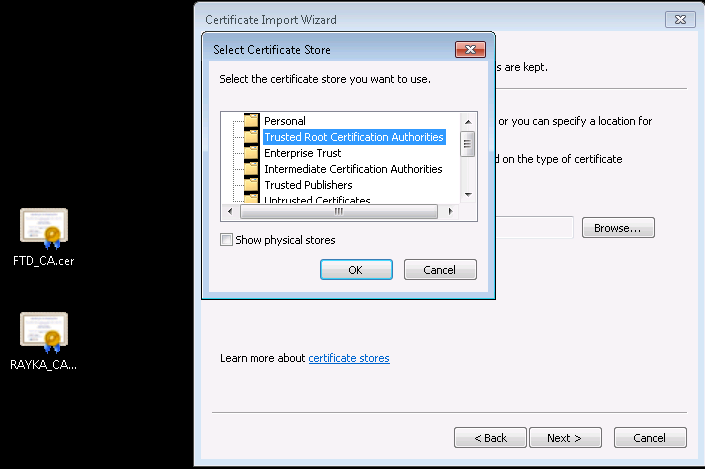
Now the Cisco FTD certificate is ready and can be used by users inside the network, but don’t forget to trust it to the computers inside the network.
Configure SSL Policy to Decrypt and Re-Sign
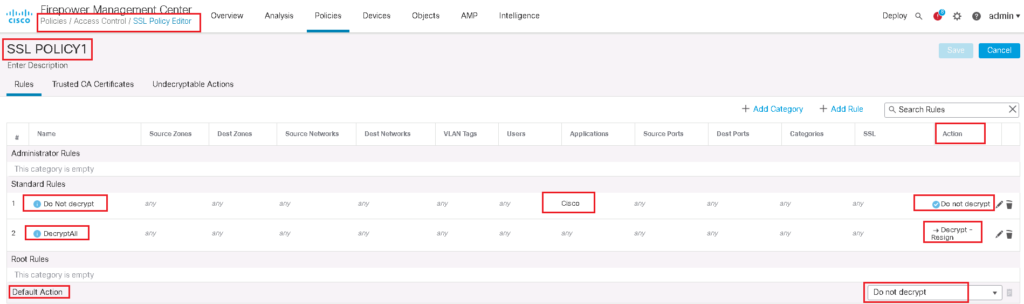
In the next step, we have to add a SSL Policy. in our example we will decrypt all https websites except cisco.com.
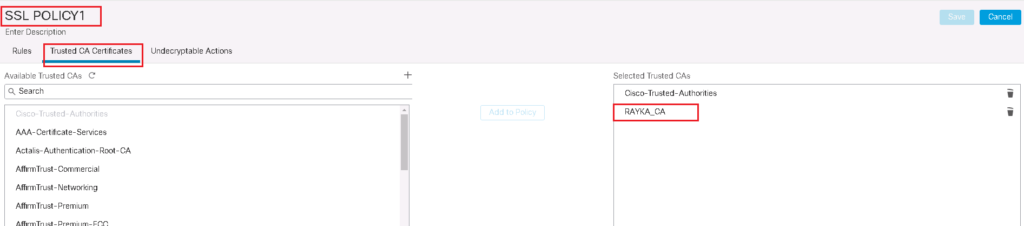
To add a new SSL policy, first do not forget to trust enterprise CA certificate in your SSL Policy.
Policies -> SSL -> New Policy -> Trusted CA Certificates
Then we add two rules.
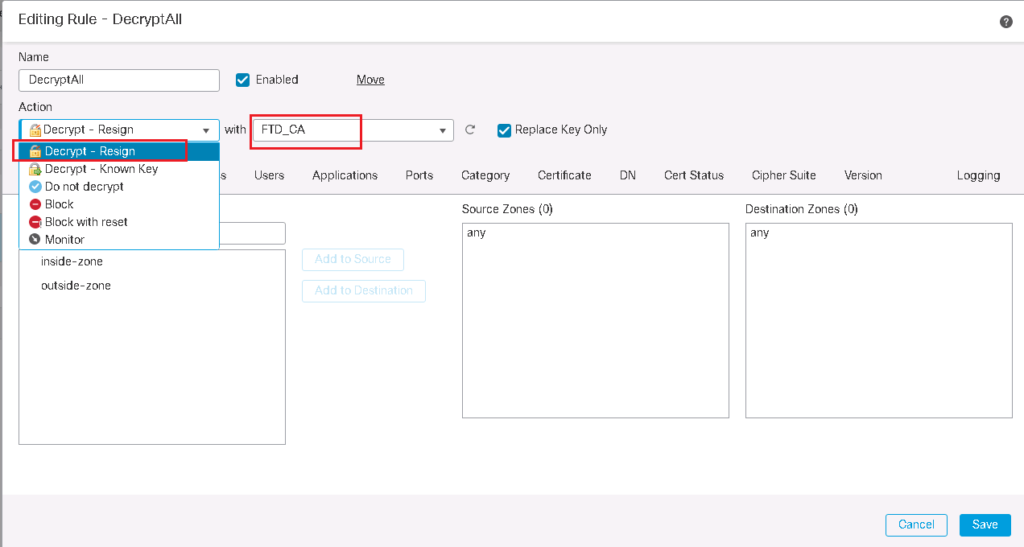
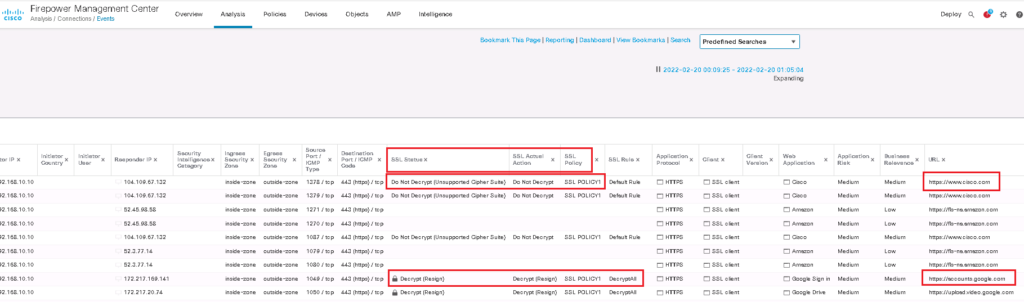
The first rule is to decrypt all SSL traffic with “Decrypt – Resign” Action. We choose FTD certificate which has to be transferred to users instead of real servers certificate. we do not forget to enable logging so we can monitor SSL traffic and corresponding policy.
In the second rule, we choose “Do not decrypt” action for cisco application. So we expect that cisco.com traffic will not be decrypted. To monitor cisco.com traffic, we enable logging also in this rule.
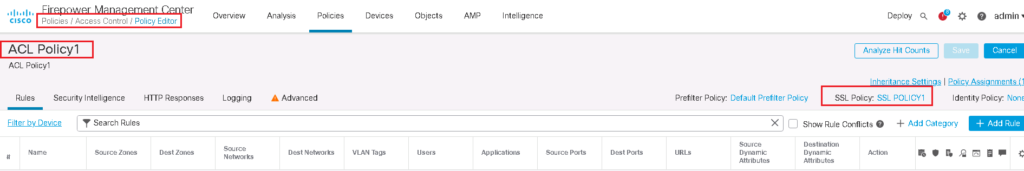
Enable SSL Policy in Access Control Policy
SSL Policy will not work until it is activated in Access Control Policy.
Test, Monitor and Troubleshoot the “Decrypt Re-Sign” SSL Decryption Policy
Now we can check HTTPS websites from computers inside the network to evaluate our SSL Policy.
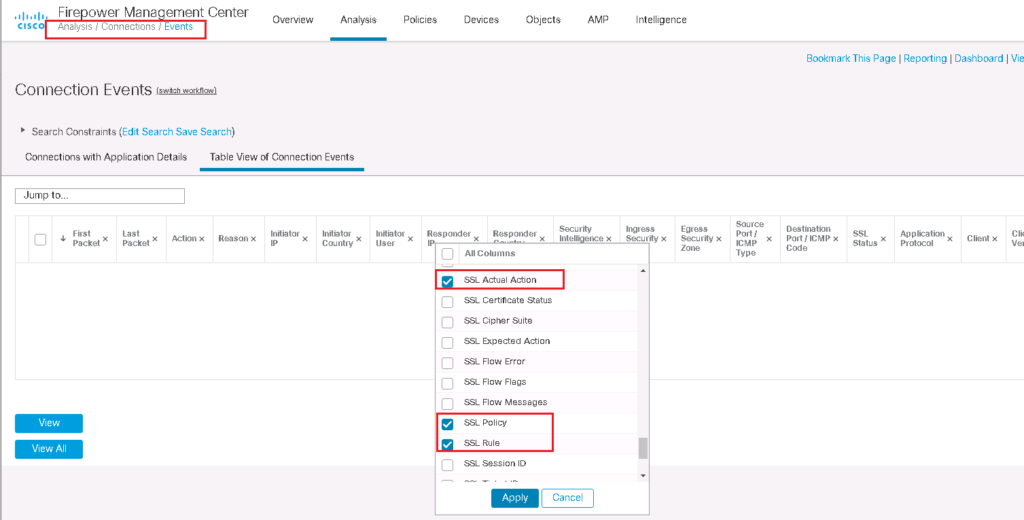
I add three fields in conenction events regarding SSL to better monitor SSL connections.
I browse three website, google.com, amazon.com and cisco.com to check the certificate and also connection event.
We expect that user can browse amazon.com and google.com with FTD certificate but cisco.com certificate will be the real certificate from user perspective.