VXLAN Anycast Gateway is one of the new and interesting features in which gateway, unlike native Ethernet networks, is not configured at a central point and in the distribution or aggregation layer. However, the gateway is distributed and configured in each leaf or access switches to which endpoints are directly connected. In this video we are going to discuss the anycast gateway in the VXLAN network in more detail.
what is anycast?
What is anycast? Anycast addresses allow you to set the same IP address in multiple points in the network without getting the duplicate address error. anycast address is normally used for redundancy purposes. When you connect to an anycast address, you will be connected to the nearest one. nearest in the network means the best path in IGP or BGP or who answers the ARP request earlier if they are configured in the same LAN.
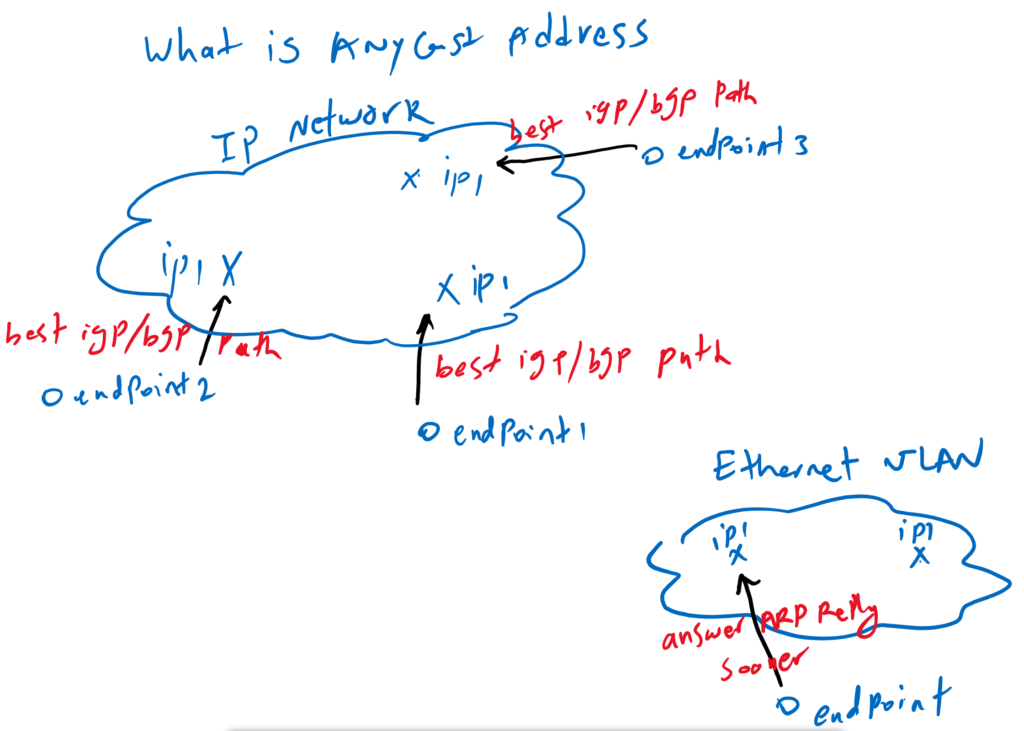
As you can see in the above part of the topology, the IP1 address is configured at three points on the network using the IGP/BGP routing protocol. from IGP/BGP perspective, we have three path to reach to the same IP. so every router in the network chooses it’s own best path for reaching IP1 address. When endpoints connect to this IP, the endpoint’s gateway chooses the best path from the IGP/BGP perspective to reach IP1 address.
In the lower part of the topology, IP1 address is configured at two points but in the same VLAN. IGP/BGP play no role in choosing the best path since they are in the same LAN. In the LAN, endpoints connect to the IP that reply to ARP requests earlier.
VXLAN Anycast Gateway
Now that we know what an anycast address is, we can discuss how the gateway configuration differs in a traditional network with a VXLAN network.
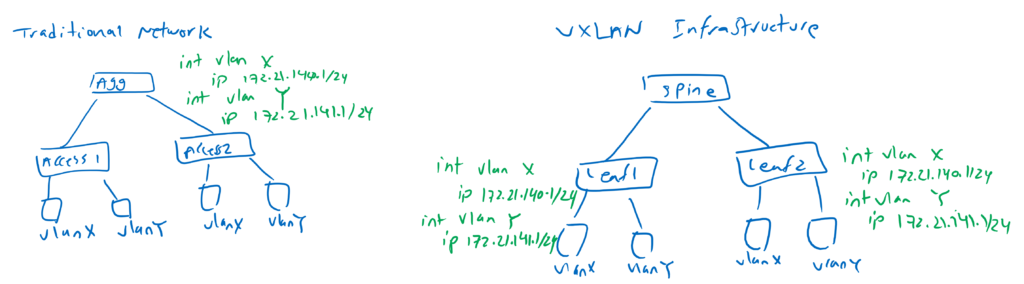
In traditional network, Gateways are configured centrally in the distribution or aggregation layer. in VXLAN network, Gateways are configured distributed and in leaf switches.
In traditional network, inter-VLAN traffic is forwarded through central distribution or aggregation layer switch if endpoints are in the same local access switch. But in leaf and spine architecture, traffic is routed always in local leaf switch. So the traffic is not forwarded through spine switch if source and destination are in the same switch
inter-vlan traffic flow in VXLAN network
In traditional network, inter-VLAN data traffic is forwarded through a central distribution or aggregation layer switch even if the endpoints are in the same local access switch.
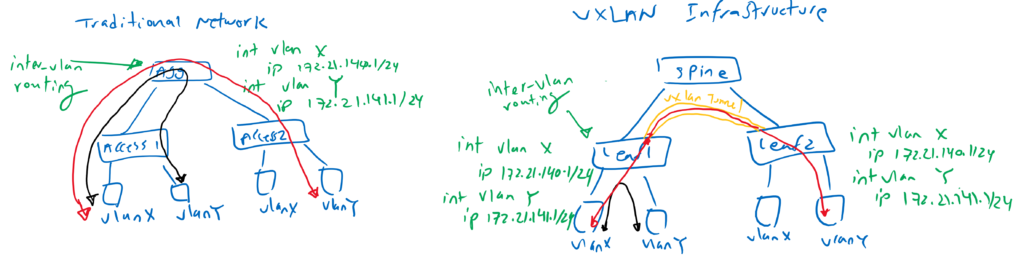
In the leaf and spine architecture, however, the traffic is always routed in the local leaf switch. The data traffic is therefore not forwarded via the spine switch if the source and destination are in the same leaf switch
Anycast Gateway Configuration
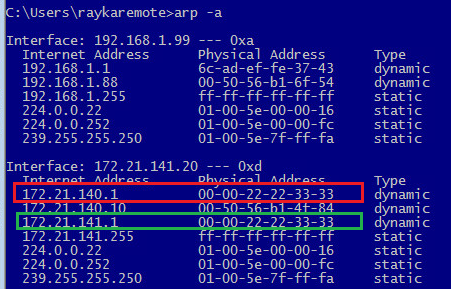
The sample configuration of anycast gateway is shown here. Exact the same IP address is configured in all leaf switches. Then anycast-gateway is enabled in each “interface vlan” so you will not receive duplicate address error since in a normal LAN environment, you are not allowed to configure the same IP Address in multiple nodes.
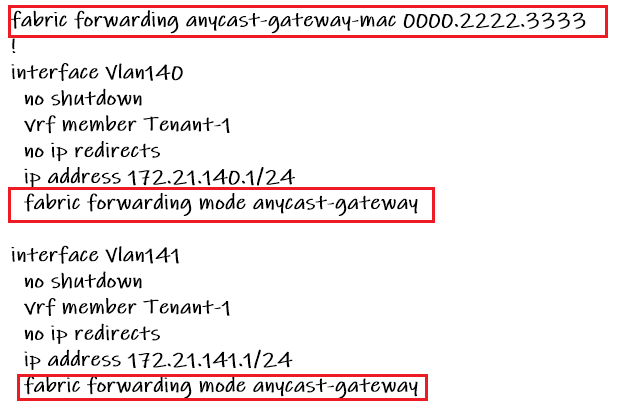
As you can see in the configuration, not only is the gateway IP address configured as an anycast address, but the gateway MAC address is also configured as an anycast address.
Another point with anycast MAC is that it can be the same for all VLANs, since the MAC address is locally significant in each VLAN.
The ARP table of an endpoint that has links in both VLAN 140 and VLAN 141 is displayed here. As you can see, the gateway’s MAC address in both VLANs is the same as we configured in the leaf switches.