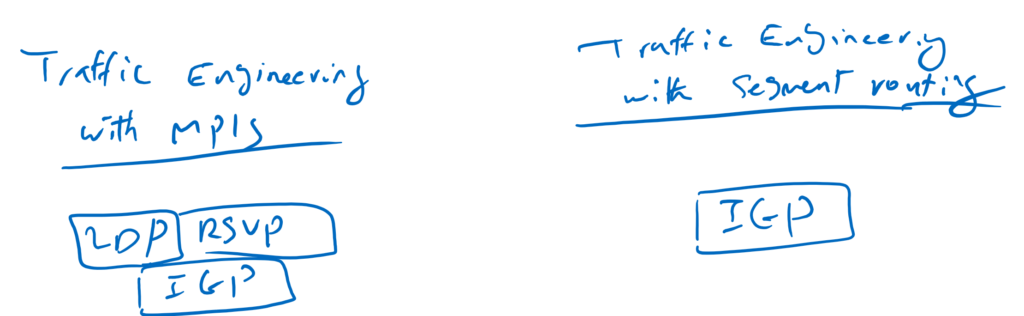This is the first video of the segment routing course, and the first question that arises is what is segment routing? To better explain what segment routing is and how it works. It can be a good idea to compare how traffic is forwarded on the IP network, MPLS network, and also segment routing capable network.
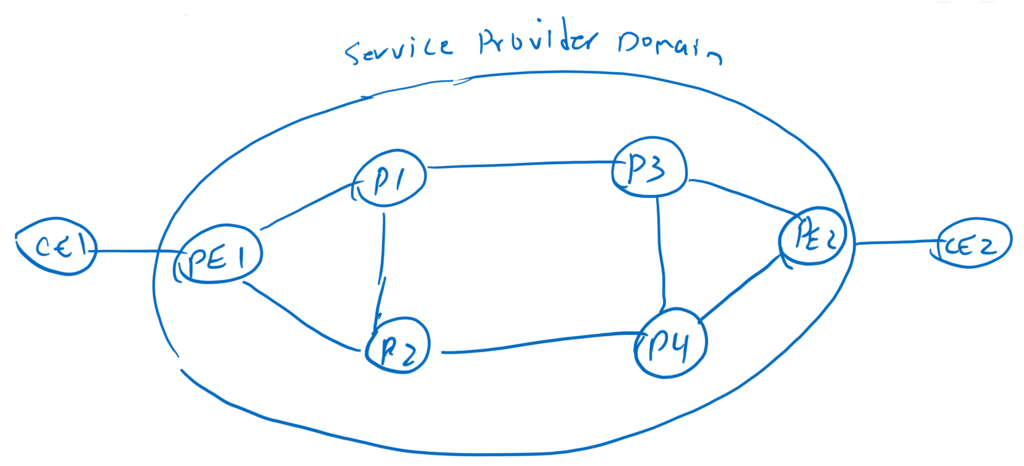
Topology to compare IP versus MPLS versus Segment Routing
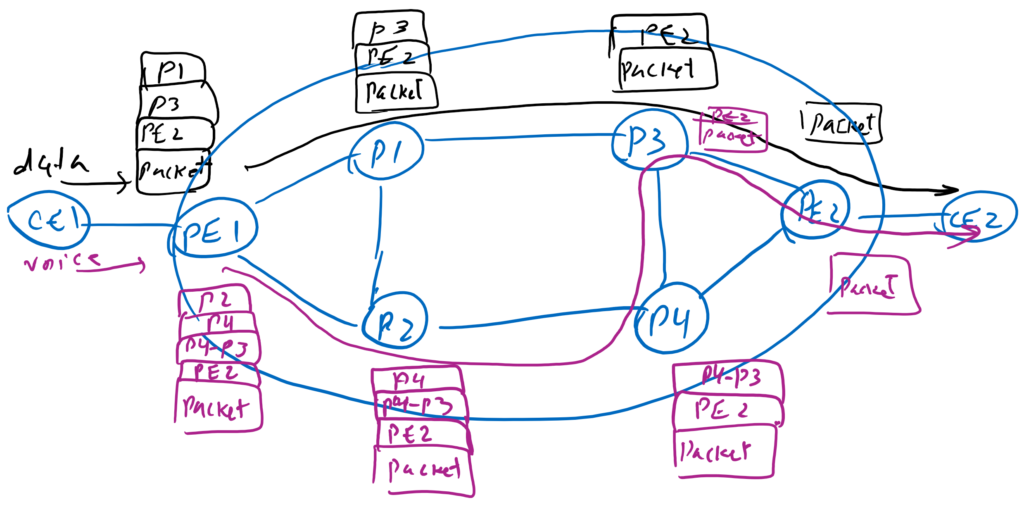
In the following figure, two CE routers connected to provider PE routers want to communicate through the provider network. As you can see, the provider has many path options to move the traffic from the source to the destination. From above, from below or partly from below and partly from above. Depending on the Topology, the options can be more or less.
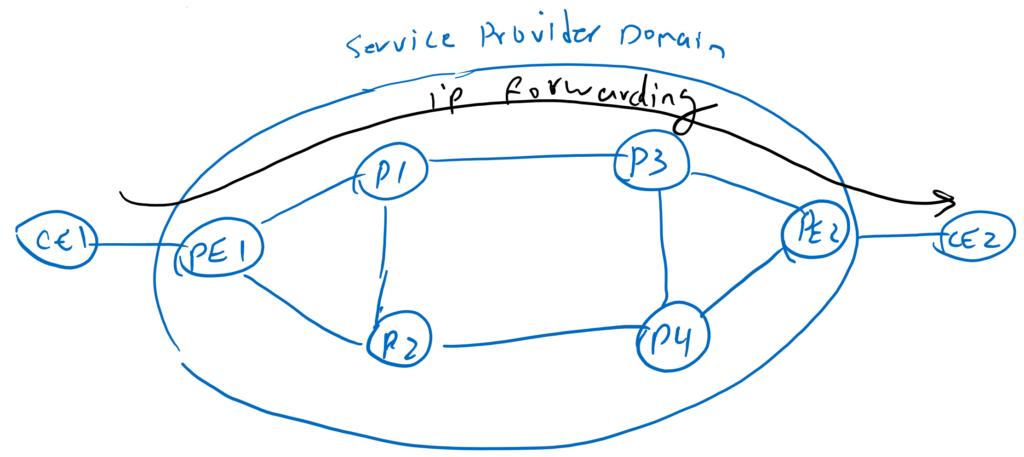
Forwarding in IP Networks
When forwarding in the IP network, the data traffic always goes over a certain path, which is best path chosen by IGP. Here we assume it goes from above, PE1-P1-P3-PE2 and then destination. One problem we face in such networks is that traffic will not be directed to another path when that path is congested, however that path is the best path. Another problem is that you cannot route your voice and data traffic through different path. the requirements for data traffic and voice traffic are different. The data traffic requires high bandwidth, but the voice traffic requires minimal delay.
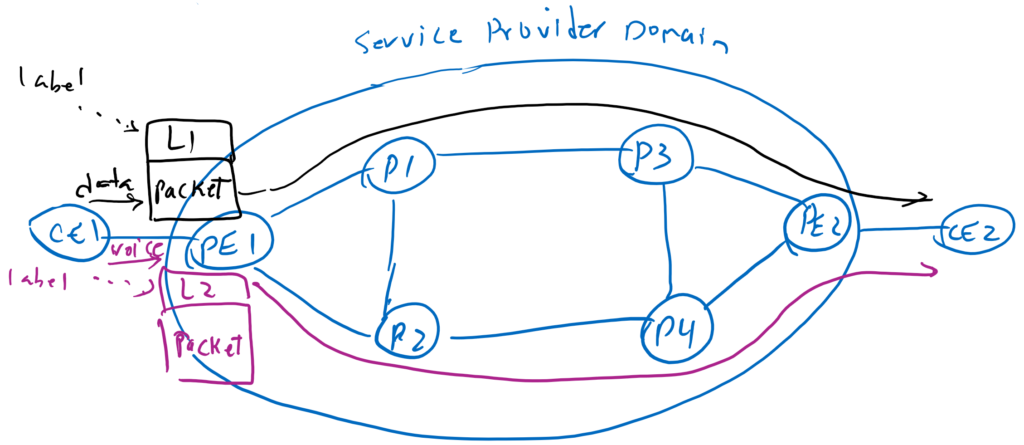
Forwarding in MPLS Network
When forwarding in the MPLS network, when PE1 receive traffic from CE, adds a label above the data traffic that shows the entire path and all routers in the path know this label and the corresponding path. The traffic is therefore forwarded via a certain predefined path. In fact, in an MPLS network, by changing the label on the edge of the network, we can control the entire path of the traffic. This is the advantage of MPLS, which makes it possible to isolate the data plane from the control plane.
For example, if we add the label L1 above the packet, all the routers in the path will know that the packet must be forwarded from the above path and if we add label L2 then all the routers in the path will know that the packet must be forwarded from the below path.
The advantage of MPLS networks over IP networks is that we can easily route voice and data traffic through different paths when required depending on their QoS requirements.
The disadvantage of MPLS networks is that all routers must maintain the state of all paths. Data traffic with the same IP destination but with different labels must be forwarded through different path and all routers need to know that.
Forwarding in Segment Routing Network
and how is the forwarding in segment-routing networks. With segment routing, just like with MPLS, we control the path of the traffic at the edge of the network. The difference, however, is that the path is maintained in the packet itself and not in routers in the path.
For example when a data packet arrives at PE1, it decide to send the traffic through P1-P3-PE2 to the destination. So it add router-id of routers (segments) in the order above the packet and then forward the packet to the first hop specified in the packet. When first router, receive the packet, it find the next router through the packet itself and so the router does not need to maintain the information of many path.
As you have seen, segment is actually the router-id of the router. But the reality is that we have different type of segment. For example a link can also be a segment.
prepare your own “segment routing” laboratory
For example when a voice packet arrives at PE1, it decide to send the traffic through P2-P4-P3-PE2 to the destination. So it add maybe in addition to router-id of routers, the id of some links, here P4-P3 Link (which is another type of segment) above the packet and then forward the packet to the first hop specified in the packet. When first router, receive the packet, it find the next router or some specific link through the packet itself and so the router does not need to maintain the information of many path.
Segment Routing vs MPLS
With segment routing, like MPLS, we control the path of different applications according to their QoS requirements, but at a lower cost. because the routers in the network do not have to maintain the state of every path.
In other words, to do traffic engineering in MPLS, in addition to IGP, we need LDP or RSVP for path signaling. but with segment routing we don’t need LDP or RSVP, and IGP with some extensions is enough for segment routing.