VXLAN technology is used in the leaf and spine architecture and not in the traditional access aggregation network architecture. In this video, we compare these two technologies and discuss the advantages of the leaf and spine architecture.
what is VXLAN EVPN Technology?
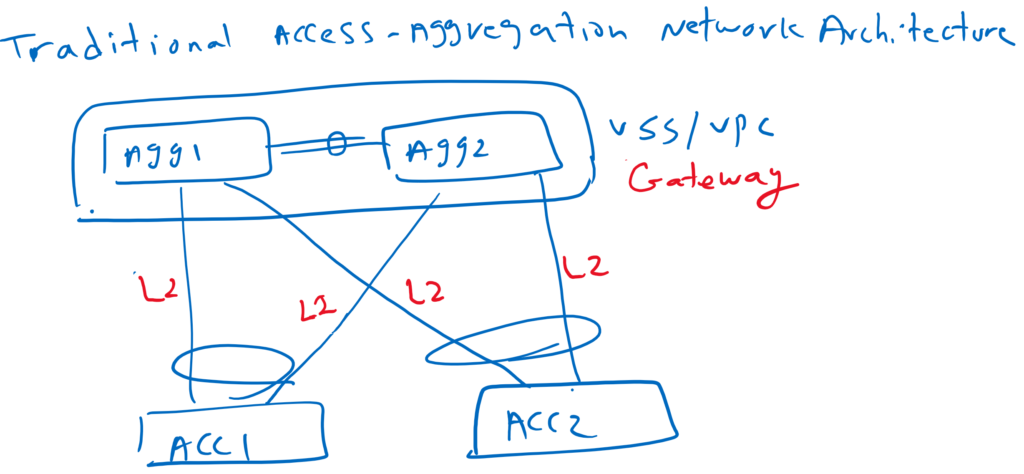
Traditional access-aggregation Network Architecture
Just to review, as you know, in the access aggregation architecture, each access switch is connected with two aggregation switches at best. Due to switch redundancy technologies like VSS and VPC, we cannot have more than two aggregation switches. The connection between access and aggregation switches are L2 connections and gateways are configured in aggregation switches.
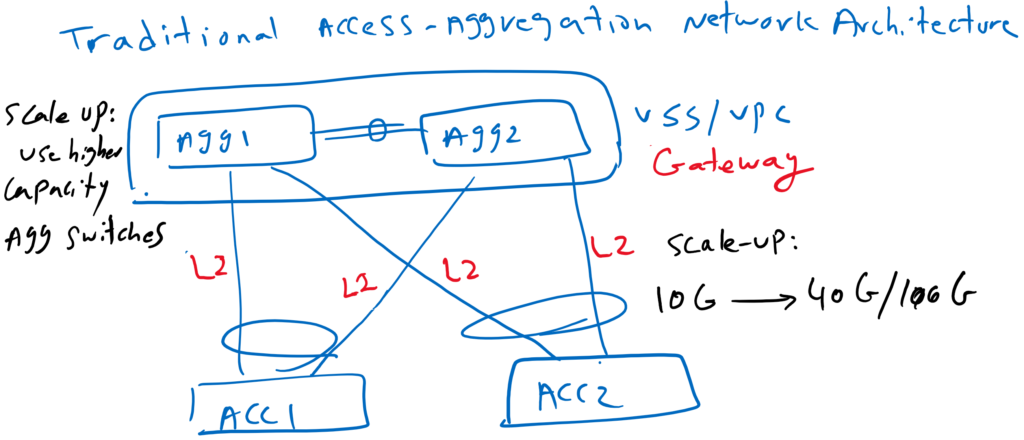
In the access aggregation architecture, scale-up is the method of scalability. That means, when we have capacity problem on the network, the solution is to increase the link or switch capacity. For example, the link speed between access and aggregation switches can be increased from 10G to 40G or 100G or we can use the switches with higher capacity in aggregation layer. As you know, the scale-up method cannot scale enough if the traffic increases unexpectedly in a short period of time.
Leaf and Spine Network Architecture
In leaf and spine architecture, servers and end users are connected to leaf switches like access switch in traditional architecture. leaf switches are connected to spine switches which are similar to aggregation switches. all leaf switches are connected to all spine switches and there is no connection between leaf switches and also no connection between spine switches except for special cases.
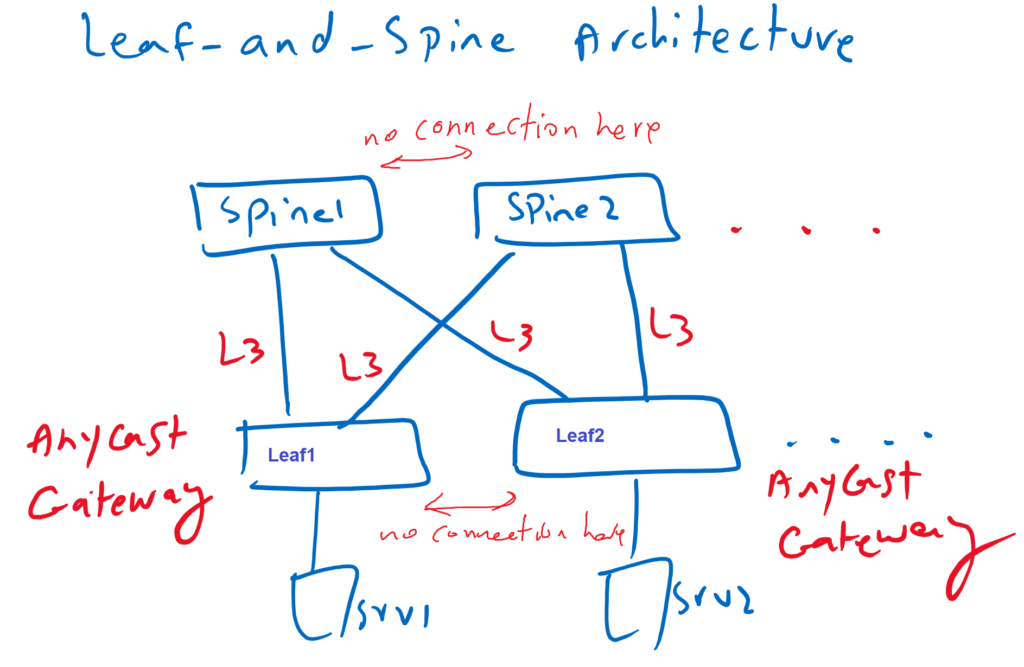
all links between leaf and spine are L3 links and they are used simultaneously without using LACP aggregation protocol and no link is blocked because of STP protocol since there is no STP protocol in L3 links. in this architecture, all east-west traffic or traffic between server are load shared through all spine switches and always there are three hops between endpoints.
In leaf and spine architecture, gateways are anycast and are configured in all leaf switches. That means for each VLAN, the same gateway IP address is configured in all leaf switches without overlapping problem and endpoint can access it’s gateway in the connecting leaf switch.
Also there is no limitation with the number of spine switches and we can increase the capacity of the network with increasing spine switches.
As you have noticed the biggest advantage of this architecture is the scale out methodology of scalability. That means, with adding new spine switch in the network, we can create new path and so new capacity. This is in addition to the scale-up methodology that is also present in this architecture.
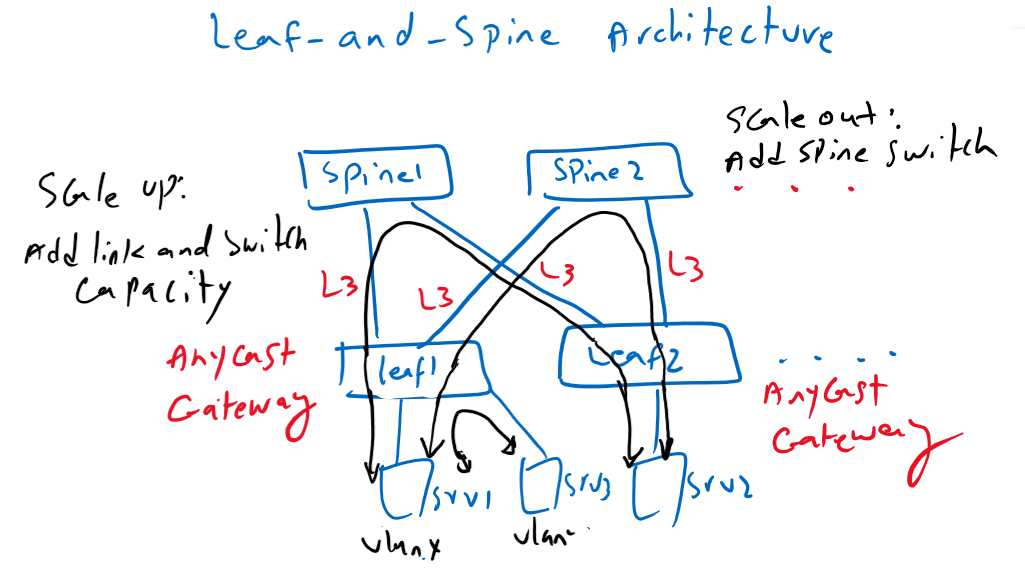
In this architecture, local traffic is always switched locally, even if it belongs between servers in different VLANs, since gateways are located in the connecting leaf switches.
As we have said, we are discussing leaf and spine architecture since VXLAN technology is used over leaf and spine architecture.