Segment routing multi domain is the discussion of this video which makes segment routing traffic engineering possible in multi domain networks. Also we will see how and why new PCE component (Path Computation Element) is used to calculate traffic engineering dynamic path instead of source PE routers.
As you can see in the picture, we have a network with two domains. An isolated ISIS process is running in each domain. The routers in each domain only know the topology of their own domain. Now the question arises, how is it possible to find dynamic segment routing traffic engineering path between PE routers when they do not see the entire topology of the network.
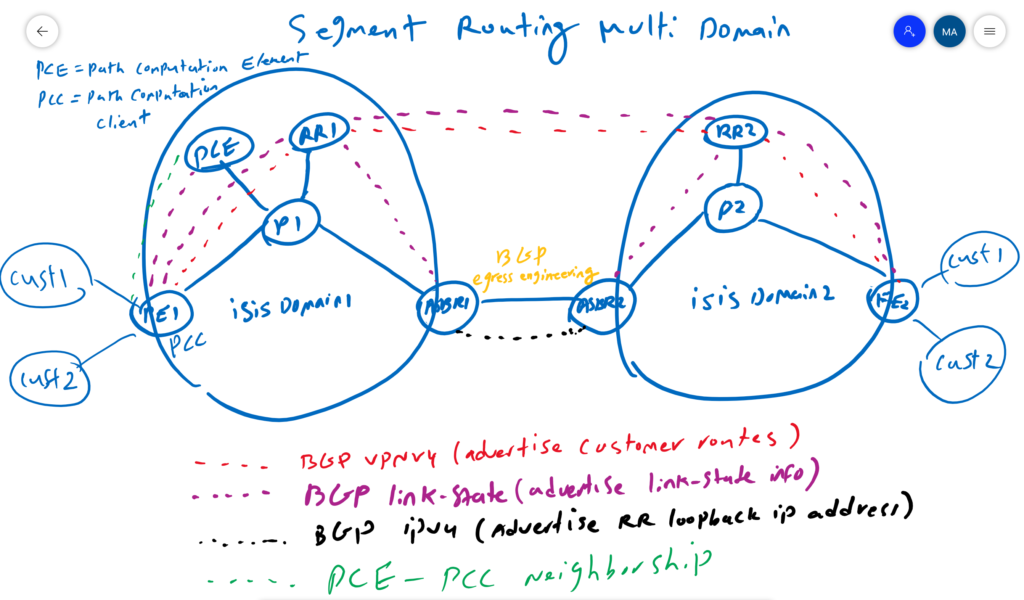
this is exactly the question that we want to answer in this section. there are different components which help to answer this question.
First, BGP VPNV4 address family which advertise customer routes between PE routers and through route reflector which is shown here by red color. Make this to happen, RRs in two domain must be able to see each other.
To make RRs in two domain to reach each other, we create BGP IPV4 address family between ASBR routers in two domains, shown by black color. The only address that is advertised between two domains and through the BGP IPv4 address family is the IP address of the loopback interface of RRs.
What is probably new to us is the new BGP address family called “Link-State” address family, which advertises link state information or topology information through BGP, which only ISIS and OSPF could possibly already do.
In this network, in order to make the topology of each domain known to another domain, the topology of each domain is advertised to another domain through RRs and BGP link state address family.
In each domain at least one router is responsible to distribute ISIS or OSPF topology information to BGP protocol. Here, I have chosen PE routers to do this but it can be any router in the domain. Here with purple color, it is shown that PE routers advertise topology information to RR through BGP Link-State address-family. RRs advertise these information between domains. now at least one router in addition to RR in each domain knows the topology information of both domain.
Do not forget that the router that knows the topology of both domains can be a different router than PE routers. so the question is how PE routers can calculate dynamic traffic engineering path in segment routing network when they do not know the topology information of the network. so here new PCE component comes to play.
Topology information must also be made known to the PCE router, which is responsible for dynamic path calculation instead of the PE routers. PE routers as PCC (Path Computation Client) request PCE with PCEP protocol to find a dynamic path when they receive a route with specific color that matches an ODN policy in the same PE router.
PCE also informs PCC of any topology change with new path information. the communication between PCC and PCE is shown here with green color which is PCEP or Path Computation Element Protocol.
Here since I have the topology information of both domains in the PE router, I don’t actually need a PCE component. the path can be calculated by the PE router itself. But one goal of this video was to introduce you to the PCE component in segment routing technology.
Another component that is shown between ASBRs is the configuration of “BGP Egress Engineering”. It creates an adjacency SID for the link between ASBR1 and ASBR2. It is not generated by ISIS or OSPF since these protocols are not enabled in this link. This is required to generate the adjacency SID for the links between ASBR routers so that source PE routers can choose which link to use between domains.
Refrences: